Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments in Modaomen distributary mouth of Pearl River Estuary
-
摘要:
本文测定了磨刀门河口76个表层沉积物样品中Zn、Cu、Mn、Pb、Ni、Cr、Cd7种元素的含量,并对其分布特征、来源与沉积环境的影响、风险评价等进行分析。结果表明,研究区域中的Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb、Cd元素主要源于磨刀门河口的输入,Zn和Cr则具有多种来源;沉积物粒度特征是影响Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb、Cr5种元素分布的主控因素;研究区潜在生态风险整体情况较为严重,表层沉积物的生态风险的主要由Cd元素引起。
Abstract:This paper determined the concentrations of 7 heavy metals including Cu, Zn, Mn, Ni, Pb, Cr and Cd in 76 sediment samples collected from Modaomen estuary, and analyzed the distribution characteristics, sources, effects of sedimentary environment and ecological risk of these elements. The results indicated that Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb and Cd in the study area came mainly from the Modaomen, and Zn、Cr had various sources. Characteristic of sediment grain size was the main factor that influenced the distribution of 5 elements including Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb and Cr. The potential ecological risk of the study area was generally serious, and the ecological risk of the surface sediments was mainly caused by Cd.
-
Keywords:
- Modaomen estuary /
- sediments /
- heavy metals /
- distribution characteristics /
- ecological risk
-
重金属作为水环境中最严重的污染物之一,具有环境持久性、毒性和生物蓄积性等地球化学行为特征,对生态环境具有潜在的生态危害性[1-2]。研究表明,重金属进入水体后,在不同的水环境条件(PH、盐度、温度等)下,绝大部分通过水动力作用及生物地球化学过程最终沉降到沉积物中蓄积起来[3]。当水环境条件发生变化时,沉积物中的重金属又会被释放出来,对水环境造成二次污染[4]。因此,沉积物不仅是水体重金属的重要归宿和主要存储场所,也是潜在污染受体和污染源[5]。同时沉积物作为水生生态系统最重要的生物栖息场所之一,其中的重金属容易进入食物链逐步富集和放大[6]。通常情况下,在受重金属污染的体系中,水相中的重金属含量甚微,而且随机性大,其含量分布常因排放状况与水动力条件的不同而不同。但沉积物中的重金属含量由于累积作用往往比相应水相中的含量要高,且表现出较强分布规律。河口处于海洋、淡水、陆地间的过渡区域,同时受径流、潮流和波浪等动力因子的共同作用,是水动力条件和环境参数变化最复杂的区域,也是自然资源、自然环境和人类开发活动的相互作用最活跃,是典型的生态环境脆弱区[7]。三角洲是河口地区最为典型的一类地貌单元,随着河口承纳的废污水不断增加和河口水动力条件的变化,三角洲地区富集的污染物也随之增加,而重金属是众多污染物中最严重的污染物之一。因此,河口沉积物中的重金属具有重要的环境指示意义。
磨刀门是珠江最大支流西江的入海口,是珠江的主要泄洪通道。随着社会经济的发展,珠江流域和珠江三角洲地区工业排污、农业废水、交通污染逐渐增多,特别是近年来西江上游重金属污染事件常有发生,如2012年的广西河池市龙江河段镉污染事件、2013年贺州市贺江流域的水污染事情等,在这一背景下,作为西江入海口的磨刀门,其沉积物中的重金属含量是何状态,生态风险程度如何,这些都是值得关注的问题。而近年来,鲜有专门针对磨刀门区域重金属情况的报道。鉴于此,本文拟通过在磨刀门海域密集采集表层沉积物样品,测定其中7种重金属(Zn、Cu、Mn、Pb、Ni、Cr、Cd)的含量,分析其分布特征,探讨来源和沉积环境对其分布的影响,评价其污染状况和生态风险程度,以其为磨刀门河口及珠江水系重金属污染的综合防治和生态风险管理提供有利的科学依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 样品采集与分析
于2015年3月在磨刀门河口使用抓斗式采泥器采集了表层0~5 cm深度的76个沉积物样品,采样点具体位置如图 1所示。表层沉积物的采集、运输和保存按照海洋监测规范(GB 17378) 的相关要求进行操作。
重金属元素测试所采用的仪器为电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪ICP-OES(PE Optima 5300 DV),为保证实验的准确性,选取10个样品做加标回收实验,使用的标准样品为广东水系沉积物成分分析标准物质GBW07312(GSD-12),向样品中等量加入各元素含量数值的标准物质,按实验步骤进行检测,测定加标回收率,所得各元素的回收率在90%~110%之间。同时实验通过平行样方法检测实验的分析精度,选取15个样品(样品数量的20%),每个样品做5组平行样,按实验步骤进行平行实验,所得相对标准偏差在5%以内(RSD<0.5%)。
在实验室内先用HCl-HClO4-HNO3对样品进行消解,再采用电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(ICP)测定7种重金属(Cu、Zn、Mn、Pb、Ni、Cr、Cd)的含量;
沉积物的粒度使用Mastersizer 2000激光粒度仪分析测试。
采用SPSS数据统计软件,对实验数据进行特征值、相关性、因子分析等统计分析。
1.2 污染评价方法
采用由德国学者Muller于1979年提出的地累积指数法(index of geo-accumulation)对研究区域的重金属污染累积程度进行研究,其计算公式为[8]:

(1) 式中:Cn为沉积物中重金属n的实测含量;Bn为沉积物中元素n的地球化学背景值,本文采用的珠江口沉积物重金属背景值,Cu、Zn、Mn、Pb、Ni、Cr、Cd的背景值分别为16.1×10-6、94.3×10-6、306.8×10-6、21.9×10-6、30.3×10-6、69.3×10-6、0.2 ×10-6[9-10];K为考虑当地沉积物差异可能会引起的背景值变动而取的系数(一般取值为1.5)。
采用由瑞典学者Hakanson于1980年提出的潜在生态风险指数评价方法(potential ecological risk index)[11-14]对磨刀门沉积物中重金属的潜在生态风险进行评价。其计算公式为[12]:

(2) 式中:RI为沉积物中多种重金属的综合潜在生态风险指数,是所有重金属潜在生态风险系数的总和[13]; Eri为重金属i的潜在生态风险系数;Cri为重金属i的污染系数;Ci为沉积物中重金属i的实测含量;Cni为重金属i的评价参照值,本文采用珠江口沉积物重金属背景值,Cu、Zn、Mn、Pb、Ni、Cr、Cd的背景值分别为16.1×10-6、94.3×10-6、306.8×10-6、21.9×10-6、30.3×10-6、69.3×10-6、0.2 ×10-6 [9-10];;为单个污染物的毒性响应系数[14],Cu、Zn、Mn、Pb、Ni、Cr、Cd的毒性响应系数分别为5、1、1、5、5、2、30。由于RI 的分级标准与重金属和PCB有关,本文与Hakanson的研究相比缺少PCB,故本文使用RI 的分级标准也依据Hakanson分级原则进行了适当调整(表 4)[12]。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 重金属含量与分布特征
磨刀门表层沉积物中7种重金属含量的统计值如表 1所示。就单一元素而言,含量最高的是Mn,平均含量为670.88×10-6,其次是Zn,平均含量为254.67×10-6,含量最低的是Cd,平均含量仅为0.88×10-6,7种重金属的含量大小顺序为:Mn>Zn>Cr>Cu>Pb>Ni>Cd。7种重金属中,Zn和Cd的变异系数最大,分别为60.9%和54.4%,表明两种元素的分布的差异较大,可能存在点源输入;其它几种元素的变异系数相对较小,说明来源较为一致。
表 1 磨刀门表层沉积物中重金属含量的特征值统计(×10-6)Tab. 1 Contents of heavy metals in surface sediments of Modaomen estuary(×10-6)
7种重金属元素的含量分布和沉积物粒径分布如图 2所示。Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb和Cr5种重金属的含量具有相似的空间分布规律,在拦门沙外坡5~8 m等深线之间的研究区域偏西一侧,都有一个明显的含量高值区域,Cu、Mn、Ni 3种元素的含量最大值(43、63号点)都出现在这一区域;从这一高值中心向海和向陆,5种重金属的含量都呈减小趋势;在向陆一侧的拦门沙附近,有一个明显的低值带,5种重金属的最低值都出现在这一个区域里(15、37、40、71号点);在泥湾门水道和磨刀门水道内,也有个别采样点这几种元素的含量较高,如磨刀门水道内28和32号点的Mn元素含量,泥湾门水道67号点的Cr元素含量等。
Cd和Zn元素含量的分布与其它5种元素分布有所不同。Cd元素的含量高值区出现在陆架5 m等深线的位置,与前面5种元素的高值区相比,Cd的高值区更靠近口门,同时,在东汊西汊水道的两端也出现多个Cd含量高值点,如24、32、56号采样点;Zn元素在整个区域的含量整体较低,含量高值多以点状出现,如东汊前端的24号采样点,泥湾门水道内的70号采样点,不像其它元素一样存在大范围的含量高值区。
2.2 各元素的同源性及沉积环境对分布的影响
磨刀门表层沉积物中各重金属元素之间及重金属元素与粘土粉砂含量、中值粒径的相关系数如表 2所示。在0.01检验水平上,Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb和Cr 5种元素两两之间均存在显著的正相关关系,表明这5种元素可能具有相近的来源和类似的富集特性;Zn除了与Cr显著相关外,与其它元素相关性都不显著;Cd除与Zn、Cr相关性不显著外,与其它4种元素都显著相关。在0.01检验水平上,Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb和Cr 5种元素的含量与粘土、粉砂的含量呈显著的正相关,与沉积物的中值粒径呈显著负相关,而Zn和Cd的含量与粘土、粉砂含量及沉积物中值粒径在0.01检验水平上相关性不显著,在0.05检验水平上,Cd与沉积物粉砂含量和中值粒径显著相关。
表 2 磨刀门表层沉积物中各重金属元素之间及与粘土粉砂含量和中值粒径的相关系数(n=76)Tab. 2 Correlation coefficient between heavy metal elements and content of silt and clay and the median size in surface sediments of Modaomen estuary (n=76)
为了进一步分析进入磨刀门河口沉积物中的重金属的来源及沉积环境对重金属分布的影响,本文采用因子分析方法进行对7种重金属元素进行了分析。KMO和Bartlett球形度检验表明,标准化后的数据适宜做因子分析。
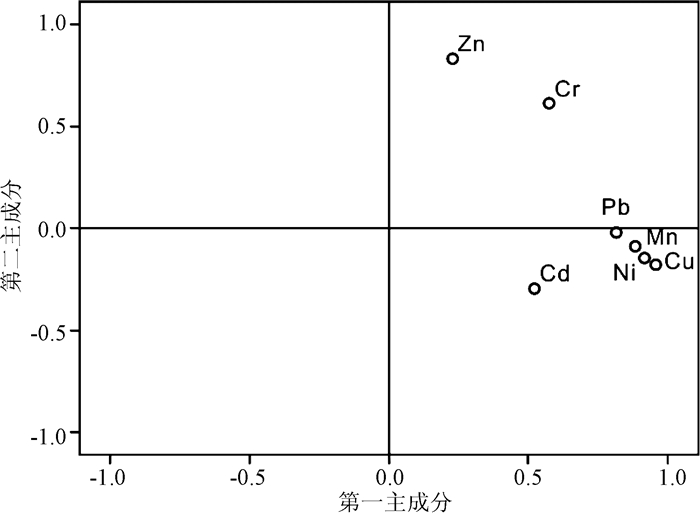
主成分分析结果表明,沉积物中7种污染物的全部信息可由2个主成分反映72.5%,即对前2个主成分进行分析已经能够反映全部数据的大部分信息。其中,第一主成分的贡献率为55.1%,Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb、Cd在第一主成分上具有较高的正载荷(图 3),表明第一主成分主要支配这5种重金属元素的来源。第二主成分的贡献率为17.4%,在第二主成分上,Zn具有很高的正载荷,而Zn元素在第一主成分呈正载荷,但值较低,第二主成分主要支配Zn元素的来源;而Cr元素在两个主成分上的载荷相当,第二主成分略高,表明Cr的来源同时受两个主成分支配。
研究区域所在的磨刀门河口,沉积物中重金属主要通过两种途径输入,一是流域排放的污染物,经干流和网河区运送,通过口门进入研究区,二是邻近海域的物质输运进入。因不同泥沙粒度特征的差异,在不同级配的沉积物中重金属的富集行为差异显著,相同环境下,泥沙越细,表面积越大,吸附作用就越强,重金属元素更容易富集[15]。第一主成分支配的5种元素中,4种元素与沉积物中粘土粉砂含量显著正相关,与中值粒径显著负相关,表明4种元素与主要源于流域径流输入的细颗粒泥沙密切相关;同时,相关研究表明,第一主成分支配的5种元素主要来自工业、农业、交通等的人类活动排放[16-18],其原始的来源差异较大,这几种原始来源不同的元素主要经干流和网河区的运送,由细颗粒泥沙携带进入研究区所在的南海陆架,因而表现出具有相似来源的特征。在磨刀门河口,河道水流携带泥沙到达口门附近,因水流扩散,流速骤减,粗颗粒泥沙开始沉降,形成拦门沙,随着流速的进一步减小,细颗粒泥沙也逐步沉降。因此,研究区域中拦门沙附近沉积物粒径最粗,向海一侧沉积物粒径逐渐变细,如图 2(h)沉积物平均粒径分布图所示。拦门沙外5 m等深线向海一侧的沉积物,平均中值粒径为14.0 μm,远小于5 m等深线以内拦门沙附近沉积物的平均中值粒径66.9 μm,而其粘土粉砂平均含量为87.1%,远大于5 m等深线以内拦门沙附近的沉积物的含量52.6%。因此,由磨刀门口门输入的Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb重金属元素的高值中心出现在拦门沙外5~8 m等深线之间的区域。Cd元素的来源也主要由第一主成分支配,但它与沉积物粘土粉砂含量、中值粒径相关性不显著,沉积物粒度特征非其主控富集因素,因此,分布规律与其它4种元素有所不同。
第二主成份反映的邻近海域物质的输入是研究区Zn元素的主要来源,同时,Zn元素变异系数较大,且高值中心呈多点状分布,受到了较大的点源污染影响。同时,河口地区水动力、盐度、PH等环境参数变化复杂,而在不同的环境参数下,悬浮泥沙对不同重金属的吸附作用不同,如悬浮泥沙对Zn、Cd的吸附受水体PH的影响较大,而对Cu和Pb的吸附受PH的影响较小[19]。Zn和Cd的分布与其它几种元素不同,除来源的因素外,还受沉积物粒径以外的其它环境因素的影响。
Cr元素的来源同时受两个主成分的支配,同时Cr元素与沉积物粘土粉砂含量、中值粒径显著相关,沉积物粒径为其主控富集因素,因此,Cr分布特征与Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb 4种元素相似。
2.3 沉积物重金属污染评价
2.3.1 地累积指数分析
表 3为磨刀门表层沉积物重金属地积累指数评价结果。从所有采样点的平均情况来看,地累积指数的大小为Cd>Zn>Cu>Mn>Pb>Cr>Ni,其中,Cr和Ni属于无污染的范畴,Cu、Zn、Pb、Mn属于轻度污染,Cd元素为偏中度污染,说明Cd是磨刀门河口区域主要的污染元素。
表 3 磨刀门表层沉积物重金属地积累指数评价结果Tab. 3 Geo-accumulation index assessment results of heavy metals in surface sediments of Modaomen estuary
对于单个采样点而言,Ni元素没有污染;其它元素都存在局部污染情况。从污染程度来看,Cd元素的污染最为严重,约有70%的采样点达到偏中度污染以上污染,部分采样点达到偏重度污染;Cu、Zn约有30%的采样点达到偏中度污染,Mn、Pb和Cr则几乎全部采样点都处于无污染到轻度污染到的程度。
2.3.2 潜在生态风险评价
由表 4表层沉积物重金属潜在生态风险指数评价结果可知,研究区93.4%的采样点潜在生态风险指数高于85,达到中等风险及以上范围,其中36.8%的采样点为达到强生态风险以上等级,区域整体的潜在生态风险为中等到强风险等级,生态风险情况较为严重。河口地区作为陆源污染物的汇集区,近年来,随着珠江流域和珠江三角洲经济的发展,人类工农业和交通排放污染物显著增加,这必然导致磨刀门等河口地区污染的加重,研究区生态风险为中等到强风险等级,也一定程度上反应了人类活动排放对河口生态系统的影响。
表 4 磨刀门表层沉积物重金属潜在生态风险指数评价结果Tab. 4 Potential ecological risk assessment results of heavy metals in surface sediments of Modaomen estuary
而从表 5中各元素的潜在生态风险系数来看,除Cd之外,其它6种元素的风险程度都为低,而Cd元素则在81.6%的采样点中生态风险达到强风险以上等级。各元素对潜在生态风险指数的贡献率从大到小分别为Cd(79.65%)>Cu(7.55%)>Pb(5.38%)>Ni(2.97%)>Zn(1.64%) >Cr(1.48%)>Mn(1.33%),虽然7种元素中Cd的含量最低,但因为其生物毒性最强,其对潜在生态风险的贡献率最大,磨刀门表层沉积物的潜在生态风险的主要由Cd元素引起。因此,磨刀门区域在今后的环境管理工作中可以将Cd作为水环境污染治理的优先控制因子。
表 5 磨刀门表层沉积物各元素潜在风险系数评价结果Tab. 5 Potential ecological risk assessment results of each element in surface sediments of Modaomen estuary
3 结论
(1) 磨刀门表层沉积物中,7种重金属的平均含量从大到小依次为:Mn(670.88 ×10-6) >Zn(254.6×10-6) >Cr(84.59×10-6) >Cu(40.08×10-6) >Pb(38.8×10-6) >Ni(29.68×10-6) >Cd(0.88×10-6);Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb和Cr5种元素存在相似的分布特征,即在5~8m等深线之间存在一个明显的高值区域,而在中心拦门沙附近区域是这几种元素的低值中心区域,Zn和Cd元素的分布则与其它几种元素有所不同。
(2) 同源性分析表明,Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb、Cd元素主要源于磨刀门河口的输入,Zn和Cr则具有多种来源;沉积环境的影响分析表明,沉积物粘土粉砂含量是影响Cu、Mn、Ni、Pb、Cr这5种元素分布的主控因素,而Zn和Cd元素的分布则主要受其它环境因子或富集特性的影响。
(3) 地累积指数反映的研究区域的污染情况为:Cd元素的污染最为严重,约有70%的采样点达到偏中度污染以上污染,部分采样点达到偏重度污染,污染程度最小的是Ni元素,所有采样点都为无污染状态,其它5种元素的污染情况则介于二者之间;潜在生态风险指数评价结果表明,区域整体的潜在生态风险为中等到强风险等级,生态风险情况较为严重;就单个元素而言,除Cd元素外,其它元素都呈低风险等级,磨刀门表层沉积物的潜在生态风险的主要由Cd元素引起,这一区域今后的环境管理工作中可以将Cd作为水环境污染治理的优先控制因子。
-
表 1 磨刀门表层沉积物中重金属含量的特征值统计(×10-6)
Tab. 1 Contents of heavy metals in surface sediments of Modaomen estuary(×10-6)

表 2 磨刀门表层沉积物中各重金属元素之间及与粘土粉砂含量和中值粒径的相关系数(n=76)
Tab. 2 Correlation coefficient between heavy metal elements and content of silt and clay and the median size in surface sediments of Modaomen estuary (n=76)

表 3 磨刀门表层沉积物重金属地积累指数评价结果
Tab. 3 Geo-accumulation index assessment results of heavy metals in surface sediments of Modaomen estuary

表 4 磨刀门表层沉积物重金属潜在生态风险指数评价结果
Tab. 4 Potential ecological risk assessment results of heavy metals in surface sediments of Modaomen estuary

表 5 磨刀门表层沉积物各元素潜在风险系数评价结果
Tab. 5 Potential ecological risk assessment results of each element in surface sediments of Modaomen estuary

-
[1] YE F, HUANG X P, ZHANG D W, et al.Distribution of heavy metals in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary, Southern China:Implications for sources and historical changes[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2012, 24(4):579-588. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(11)60783-3
[2] 刘宝林, 张鸿, 谢刘伟, 等.珠江干流表层沉积物重金属污染特征及潜在生态风险[J].东北师范大学报:自然科学版, 2015, 47(2):143-147. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBSZ201502027.htm [3] WILLIAMSON R B, VAN DAM L F, BELL R G, et al.Heavy metal and suspended sediment fluxes from a contaminated, intertidal inlet (Manukau Harbour, New Zealand)[J].Marine Pollution Bulletin, 1996, 32(11):812-822. doi: 10.1016/S0025-326X(96)00044-6
[4] 林祖亨, 梁舜华.珠江河口的现代沉积环境与底质重金属的含量分布[J].海洋通报, 1995, 14(4):43-49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HUTB199504005.htm [5] 朱青青, 王中良.中国主要水系沉积物中重金属分布特征及来源分析[J].地球与环境, 2012, 40(3):305-313. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201203003.htm [6] 吕书从, 张洪, 单保庆, 等.海河流域主要河口区域沉积物中重金属空间分异及生态风险评价[J].环境科学, 2013, 34(11):4204-4210. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201311010.htm [7] 崔伟中.珠江河口水环境时空变异对河口生态系统的影响[J].水科学进展, 2004, 15(4):472-478. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ200404013.htm [8] MULLER G.Index ofgeoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River[J].Geochemical Journal, 1969, 2(3):108-118.
[9] 马玉, 李团结, 高全洲, 等.珠江口沉积物重金属背景值及其污染研究[J].环境科学学报, 2014, 34(3):712-719. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201403023.htm [10] 杨永强. 珠江口及近海沉积物中重金属元素的分布、赋存形态及其潜在生态风险评价[D]. 广州: 中国科学研究生院(广州地球化学研究所), 2007. [11] 谢文平, 王少冰, 朱新平, 等.珠江下游河段沉积物中重金属含量及污染评价[J].环境科学, 2012, 33(6):1808-1815. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201206006.htm [12] HAKANSON L.An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control.A sedimentological approach[J].Water Research, 1980, 14(8):975-1001. doi: 10.1016/0043-1354(80)90143-8
[13] 罗燕, 秦延文, 张雷, 等.大伙房水库表层沉积物重金属污染分析与评价[J].环境科学学报, 2011, 31(5):987-995. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX201105014.htm [14] 徐争启, 倪师军, 庹先国, 等.潜在生态危害指数法评价中重金属毒性系数计算[J].环境科学与技术, 2008, 31(2):112-115. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS200802029.htm [15] 王志文. 感潮河网地区重金属数学模型研究[D]. 南京: 河海大学, 2004. . [16] 宋美英. 珠江河口水体和沉积物中重金属的分布特征及风险评估[D]. 广州: 暨南大学, 2014. [17] GRAY C W, MCLAREN R G, ROBERTS A H C, et al.The effect of long-termphosphatic fertiliser applications on the amounts and forms of cadmium in soils under pasture in New Zealand[J].Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 1999, 54(3):267-277. doi: 10.1023/A:1009883010490
[18] FACCHINELLI A, SACCHI E, MALLEN L, et al.Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils[J].Environmental Pollution, 2001, 114(3):313-324. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00243-8
[19] 张恩仁, 张经.长江河口悬浮物对几种金属吸附的pH效应[J].海洋与湖沼, 2001, 34(3):267-273. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYFZ200303004.htm -
期刊类型引用(15)
1. 阳峰,陆野,李诗颖,林振文,郑思琦,罗俊超,郭峰. 横琴粤澳深度合作区海域表层沉积物微量元素地球化学特征. 中国地质调查. 2024(06): 76-85 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郑敏慧,白冬锐,张涛,陈坦,王洪涛,杨婷,张冰,金军. 苏州水网地区河道底泥的重金属分布特征与污染风险. 环境科学. 2023(01): 198-209 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 马超群,李正炎,胡泓,王秀海,赵晓明,沈佳峰. 基于盐度校正的中国河口铜水生生物水质基准研究. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(03): 82-97 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张虹,徐敏,丁言者,徐文健,李艳霞. 小型河口沉积物重金属风险概率与主要贡献因子研究——以江苏中山河为例. 南京师大学报(自然科学版). 2023(01): 64-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李伟,孙晶,熊健,张娜,高海涛,张强英,吕学斌. 西藏拉鲁湿地表层土壤重金属分布特征和风险评价. 环境科学与技术. 2023(01): 92-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 夏嘉,高苑,王思波,王遥平. 雷州半岛近海表层沉积物重金属污染评价. 海洋环境科学. 2022(02): 276-282 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 齐莎莎,张敏霞. 海洋石油开发周边海域重金属锌的时空分布特征研究. 油气田环境保护. 2022(01): 21-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 阎琨,庞国涛,李伟,毛方松. 广西茅尾海入海河口表层沉积物重金属分布及风险评价. 物探与化探. 2022(04): 1030-1036 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 付涛,梁海含,牛丽霞,党浩铭,陶伟,杨清书. 夏季珠江口沉积物-水界面重金属分布特征及其影响因子研究. 海洋学报. 2022(10): 182-192 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 廖宝淦,刘秋辛,贾珍珍,李适宇,胡嘉镗. 珠江口磨刀门水体中重金属分布、分配特征及其影响因素. 海洋环境科学. 2021(01): 8-15 .  本站查看
本站查看
11. 李嘉怡,董汉英,牛丽霞,杨清书,罗向欣,张涛. 珠江虎门河口夏季悬浮物中重金属分布特征及其风险评价. 海洋环境科学. 2021(02): 184-189+199 .  本站查看
本站查看
12. 卢霞,范礼强,包诗玉,张雨,费鲜芸. 海州湾连岛周边海域沉积物重金属污染评价. 海洋环境科学. 2020(04): 570-575 .  本站查看
本站查看
13. 付淑清,韦振权,袁少雄,熊海仙,郭亿华. 珠江口沉积物与土壤的重金属特征及潜在生态危害评价. 安全与环境学报. 2019(02): 600-606 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 梅瀚杰,胡文锋. 黑水虻对有害物质的降解作用研究进展. 饲料工业. 2019(20): 59-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 陈碧珊,苏文华,罗松英,莫莹,刘潮明. 雷州半岛红树林土壤重金属空间分布特征及来源分析. 海洋环境科学. 2018(06): 922-928 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载: