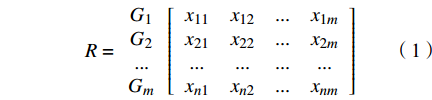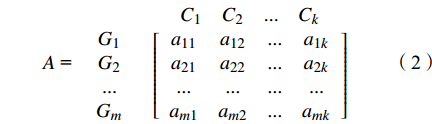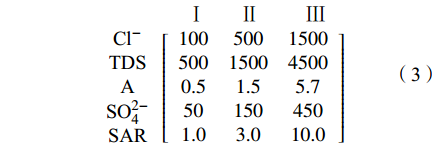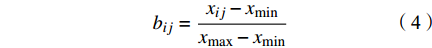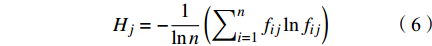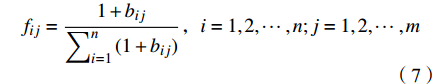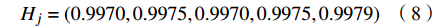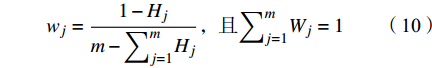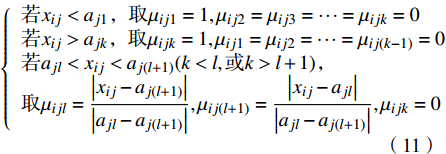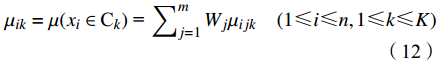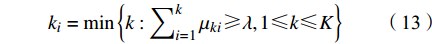Evaluation of seawater intrusion degree in Xingcheng city, Liaoning province by entropy weight method and attribute recognition model
-
摘要:
本文根据兴城地区野外调查与测试结果,选取了Cl−、TDS、SO42−、A和SAR 五项地下水化学因子作为评价指标,运用熵权属性识别法对兴城市海水入侵程度进行了评价。结果表明:研究区内42%的采样点为轻度入侵,4%的采样点为严重入侵;轻度入侵区主要分布于黑泥坑−中兴−庙后头村一带、狐狸套−王家河子村一带以及烟台河、东沙河、兴城河的河口地段,严重入侵区主要分布于周家窝铺−庆屯−海套村一带;经验证,该评价结果与氯离子单指标法评价结果的一致率达66%,而熵权属性识别法能更准确评估海水入侵的范围和程度。评价结果可为研究区海水入侵的防治以及地下水资源的可持续利用提供科学依据。
Abstract:Based on the results of field survey and sample testing,we select five groundwater chemical factors (Cl−, TDS, SO42−, A and SAR) as evaluation indices and uses the entropy weight–attribute recognition method to evaluate the degree of seawater intrusion in Xingcheng city, Liaoning province, China. Results show that 42% of the 50 sampling sites are mild seawater intrusion degree and 4% are serious degree. Mild intrusion areas are mainly distributed in the Heinikeng-Zhongxing-Miaohoutou village, the Hulitao-Wangjiahezi village ,the estuaries of the Yantai, Dongsha and Xingcheng Rivers, whereas serious intrusion areas are mainly distributed in the Zhoujiawopu-Qingtun-Haitao village. The consistency rate between the evaluation results of entropy weight–attribute recognition method and that of the chloride ion single index method is 66%, while the entropy weight–attribute recognition method can more accurately evaluate the distribution and degree of seawater intrusion. The obtained evaluation results could provide a scientific basis for preventing and controlling seawater intrusion and the sustainable utilization of groundwater resources in the study area.
-
Keywords:
- Xingcheng /
- seawater intrusion /
- entropy weight method /
- attribute recognition
-
海水入侵是外海高盐度水体沿河口河道、地下含水层向内陆入侵与渗透[1] , 导致沿海地区地下水咸化、淡水资源减少的一个不可忽视的全球性环境问题[2]。区域海水入侵程度多受水文地质条件、降水、蒸散发、径流以及风暴潮等多种自然因素影响,并往往因地下水资源开采等人为活动而加剧[3-4]。我国北方滨海地区过量开采地下水,且区域自然补给条件较差,加剧了海水入侵灾害的发展,使入侵内陆距离可从几百米扩展到几十公里[5]。因此,海水入侵程度的评价与特征分析可为研究海水入侵的形成与演化过程提供重要参考,同时为滨海地区海水入侵灾害的防治与地下水资源的可持续开发利用提供决策依据[6]。
目前,围绕海水入侵评价方法的研究已取得一些成果,其中,基于氯离子或溶解性总固体的单指标评价法在海水入侵现状评价中应用较广泛[7-8]。然而,该方法考虑因素单一,评价过程与结果易出现片面性和不确定性[9-10]。多指标综合评价法,如模糊数学法[11-12]、层次分析法[13]、集对分析法[14]以及熵权属性识别法[15]等能更全面稳定地反映海水入侵程度,相对于单指标法具有明显优势,特别是熵权属性识别法,融合了熵权法的客观赋权特点与属性识别模型的有序分割优点[16],既消除了主观赋权的偏差,又能避免最大隶属度原则的分类不清问题[17]。兴城市地处辽东湾西岸,属辽西沿海地区典型海水入侵区之一,然而该地区海水入侵现状的研究却鲜有报道。本文依据兴城市滨海地区的野外调查与室内地下水化学成分测试结果,选取氯离子(Cl−)、溶解性固体(TDS)、硫酸根(SO42−)、咸化系数(A)和钠吸附比(SAR)作为评价指标,采用熵权属性识别法对研究区的海水入侵程度进行评价,并将评价结果与氯离子单指标法评价结果对比,验证了熵权属性识别法结果的可靠性和准确性,研究结果对兴城地区海水入侵的防治与地下水资源的开发利用具有重要实际意义。
1 材料与方法
1.1 研究区概况
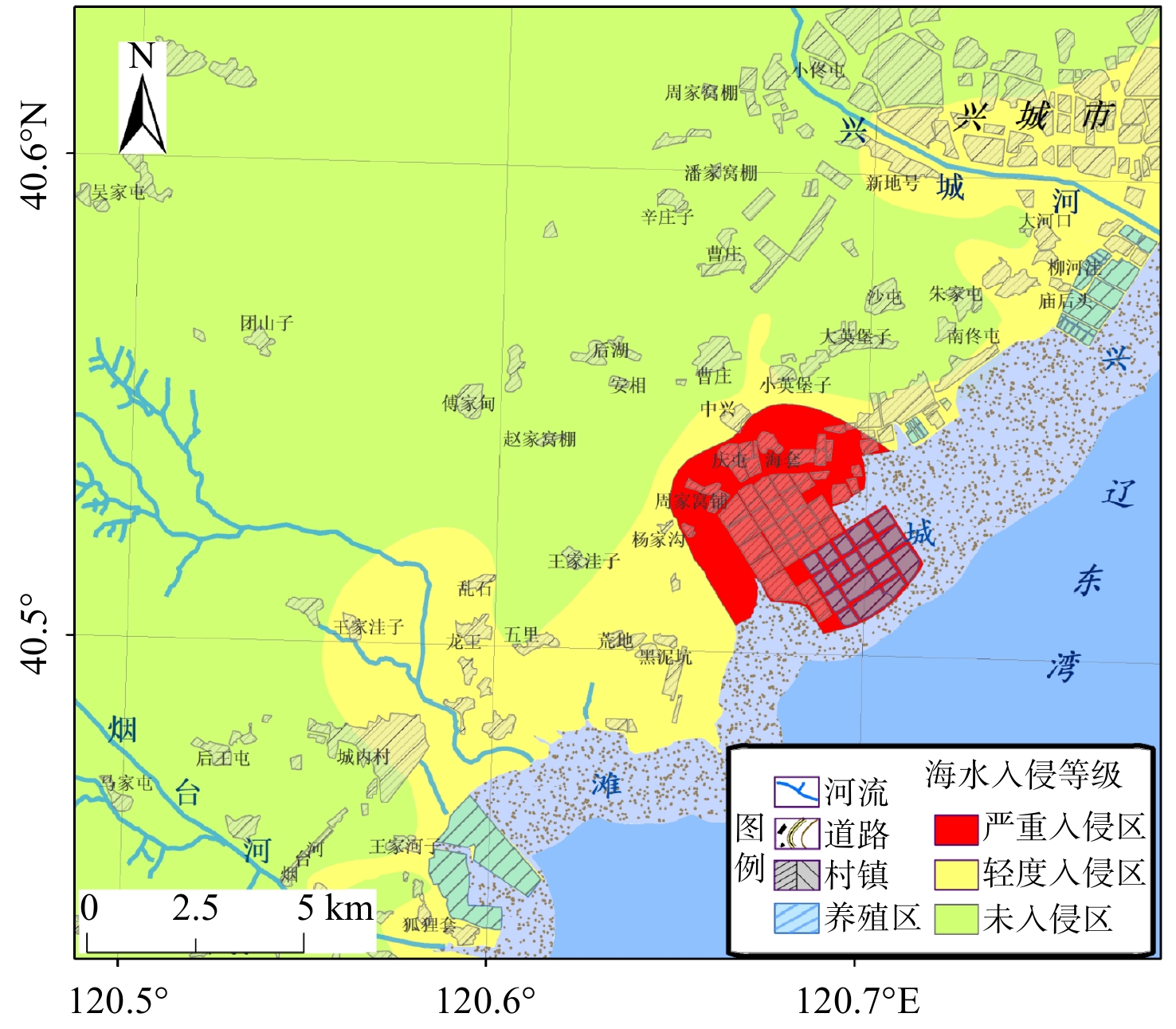
研究区位于辽宁省兴城市烟台河−兴城河的滨海地区(图1),属于冲积海积平原,地势平坦开阔,地面标高小于15 m,地面坡降小于1‰。区内属于温带半湿润季风气候,多年平均气温为9.1 ℃,多年平均降水量为619.2 mm,降水量集中在7月和8月,约占全年降水量的59%。区内含水层主要为第四系松散岩类孔隙含水层,岩性以砂砾石、砂砾卵石为主,局部中间夹有含砾亚粘土,厚度约为10~30 m。如图2所示,小甸子村−小英堡子村一带的松散孔隙含水层厚约15~20 m,上部为亚粘土,下部为砂砾石,岩性呈明显的二元结构。含水层富水性较强,主要接受大气降水、地表水及灌溉水的入渗补给,排泄方式主要为人工开采。研究区地下水基本由西北向东南方向径流,但受近年来兴城渔业快速发展的影响,天然地下水流场发生了变化,如小英堡子村和五里村一带因大量开采地下水,形成了局部地下水位降落漏斗(图1)。
1.2 样品采集与测试方法
为确定兴城滨海地区的地下水化学特征,本课题组于2019年11月垂直于海岸线方向采集地下水样50组,主要取自潜水含水层,采样深度为1~15 m,采样点分布见图1。参考《地下水质检测方法》(DZ/T0064-1993),现场采用滴定法测定HCO3−,使用多参数水质分析仪测定溶解性总固体(TDS),室内采用ICS-2100离子色谱仪(美国赛默飞公司)测定Na+、Mg2+、Ca2+、Cl−、SO42−等离子,在防灾科技学院水环境化学实验室完成测试,检测限为1 mg/L,测试精度为1%。经计算,所有水样的阴阳离子平衡误差均小于5%,可用于进一步的水化学分析,测试得到地下水化学成分的统计特征如表1所示。
表 1 地下水样品水化学特征的统计表(N=50)Tab. 1 Statistics table of water chemical characteristics of groundwater samples (N=50)测试指标 最小值/mg·L−1 最大值/mg·L−1 平均值/mg·L−1 标准差/mg·L−1 变异系数 TDS 177.00 11532.90 894.46 1830.10 2.05 Na+ 19.66 2793.31 164.18 441.97 2.69 Mg2+ 10.58 272.33 35.52 44.23 1.25 Ca2+ 25.98 737.28 111.19 105.33 0.95 Cl− 17.96 6369.00 392.17 1242.08 3.17 SO42− 17.81 1196.00 140.66 195.49 1.39 HCO3− 52.46 761.28 167.25 124.34 0.74 2 结果与讨论
2.1 海水入侵程度的熵权属性识别评价
2.1.1 选取评价指标
合理选取海水入侵的评价指标对科学客观地评价海水入侵程度尤为关键。结合研究区地下水化学成分的统计结果可知(表1),地下水中TDS、Na+、Cl−以及SO42−浓度的变异系数均大于1,空间变异性大,而Mg2+、Ca2+以及HCO3−浓度的变异系数约为1,空间变异性较明显,且以上化学成分的浓度均随着距海岸带距离的减小呈增大或减小的渐进变化规律,故能体现海水入侵程度的差异。此外,本文综合考虑了海水入侵对地下水化学成分影响的混合作用和阳离子交替吸附作用,选取了Cl−、TDS、SO42−、A以及SAR 5个代表性的评价指标,评价指标的选取依据见表2。
表 2 评价指标的选取依据Tab. 2 Selection basis of evaluation indexes评价指标 确定依据 Cl− 地下水中最稳定的离子,为判别海水入侵最敏感的指标 TDS 地下水各种离子、分子、化合物的总量(除悬浮物外),能直接体现海水与地下淡水之间的差异 SO42− 海水中较稳定的离子,地下淡水中含量较少,地下水受海水侵染后变化较敏感的指标 A 咸化系数${\text{A} } = { {\gamma ({\text{C} }{ {\text{l} }^{^\_} })}/{[\gamma ({\text{HCO} }_3^{^\_}) + \gamma ({\text{CO} }_{\text{3} }^{ { {\text{2} }^{\text{\_} } } })]} }$,其中:Cl−和HCO3−(CO32−)分别为海水与地下淡水的主要阴离子,二者比值可有效区分滨海地区的地下水类型;A是从阴离子角度分析海水入侵的程度,可反映咸淡水混合作用的强弱 SAR 钠吸附比${\text{SAR} } = { {\gamma ({\text{N} }{ {\text{a} }^ + })}/{\sqrt {0.5\gamma ({\text{C} }{ {\text{a} }^{2 + } }) + 0.5\gamma ({\text{M} }{ {\text{g} }^{2 + } })} } }$,其中:Na+是海水中首要的阳离子,其含量比地下淡水高出2~4个数量级;Ca2+和Mg2+是地下淡水中主要阳离子;SAR是从阳离子角度分析海水入侵的程度,可表征阳离子交替吸附作用的强弱 注:γ为毫克当量浓度 2.1.2 确定样本空间矩阵与属性分类标准矩阵
设评价对象空间为X,从评价对象空间取n个样本,每个样本需要测量m个指标G1,G2,G3···,Gm,第i个样本的第j个指标的测量值可表示为xij,因此,每个样本都可表示为一个向量xi=(xi1,xi2,···,xim),1≤i≤n,n个样本构成n×m阶样本空间矩阵,可表示为:
$$ R = \begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{G_1}} \\ {{G_2}} \\ {...} \\ {{G_m}} \end{array}\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{x_{11}}}&{{x_{12}}}&{...}&{{x_{1m}}} \\ {{x_{21}}}&{{x_{22}}}&{...}&{{x_{2m}}} \\ {...}&{...}&{...}&{...} \\ {{x_{n1}}}&{{x_{n2}}}&{...}&{{x_{nm}}} \end{array}} \right] $$ (1) 研究区地下水样本的海水入侵评价指标值如表3所示,受篇幅所限,本文仅给出18个样本的空间矩阵。
表 3 研究区海水入侵程度评价样本的空间矩阵Tab. 3 Spatial matrix of seawater intrusion evaluation samples in the study area编号 Cl−
/mg·L−1TDS
/mg·L−1SAR A SO42−
/mg·L−1编号 Cl−
/mg·L−1TDS
/mg·L−1SAR A SO42−
/mg·L−1F-01 144.53 492 2.07 1.26 186.53 S-01 64.20 362 1.16 0.96 102.81 F-02 215.56 519 24.64 1.50 211.12 S-02 23.11 526 1.73 0.43 121.72 F-03 33.35 177 1.15 0.63 26.85 S-03 130.12 1150 1.26 1.20 209.46 F-05 17.96 138 1.50 0.31 17.81 S-05 275.86 1090 2.80 4.86 160.75 F-07 105.04 380 1.48 1.21 88.87 S-08 33.41 200 1.31 0.52 28.39 F-17 28.06 191 1.03 0.33 60.09 S-09 6369.00 11532 31.47 183.33 1196.00 F-21 34.90 199 0.85 0.62 62.55 S-10 253.86 936 1.27 4.71 131.02 F-22 77.21 341 2.27 0.87 65.29 S-11 5479.53 4450 9.50 58.11 697.51 F-27 136.36 442 1.86 1.48 84.26 S-17 148.99 473 2.25 4.89 40.39 设F为X上的某类属性空间,(C1,C2,C3···Ck)为F的有序分割类,且满足C1<C2<C3<···<Ck,评价指标的分级标准已知,故分级标准判断矩阵可表示为:
$$ A{\text{ = }}\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {}&{\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{C_1}}&{{C_2}}&{...}&{{C_k}} \end{array}} \\ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{G_1}} \\ {{G_2}} \\ {...} \\ {{G_m}} \end{array}}&{\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{a_{11}}}&{{a_{12}}}&{...}&{{a_{1k}}} \\ {{a_{21}}}&{{a_{22}}}&{...}&{{a_{2k}}} \\ {...}&{...}&{...}&{...} \\ {{a_{m1}}}&{{a_{m2}}}&{...}&{{a_{mk}}} \end{array}} \right]} \end{array} $$ (2) 矩阵中ajk表示第j个指标在属性空间F上的第k个分割值,且满足aj1<aj2<···<ajk或aj1>aj2>···>ajk。参照《海水入侵监测与评价技术规程》(HY/T 0314-2021)、《地下水质量标准》(GB/T 14848-2017)等相关文献,确定了各评价指标的等级范围及代表值,其中,代表值依据距离判别法计算得到,由此将海水入侵程度划分为3级(表4),根据式(2),各样本属性分类的标准矩阵如下:
表 4 海水入侵评价指标的分级标准及代表值Tab. 4 Classification criteria and representative values of seawater intrusion evaluation indexes评价指标 无入侵Ⅰ级 轻度入侵Ⅱ级 严重入侵Ⅲ级 等级范围 代表值 等级范围 代表值 等级范围 代表值 Cl−/mg·L−1 <250 100 250~1000 500 >1000 1500 TDS/mg·L−1 <1000 500 1000~3000 1500 >3000 4500 A <1.0 0.5 1.0~3.6 1.5 >3.6 5.7 SO4−/mg·L−1 <100 50 100~300 150 >300 450 SAR <2.0 1.0 2.0~6.7 3.0 >6.7 10.0 $$ \begin{array}{c}\begin{array}{ccc}\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\text{Ⅰ}}&\;\;\; {\text{Ⅱ}}&\;\;\;\;\;\; {\text{Ⅲ}}\end{array}\\ \begin{array}{c}{\text{Cl}}^{-}\\ \text{TDS}\\ \text{A}\\ {\text{SO}}_{\text{4}}^{{2-}}\\ \text{SAR}\end{array}\left[\begin{array}{ccc}100& 500& 1500\\ 500& 1500& 4500\\ 0.5& 1.5& 5.7\\ 50& 150& 450\\ 1.0& 3.0& 10.0\end{array}\right]\end{array} $$ (3) 2.1.3 熵权法确定各指标的权重
熵是系统无序程度的度量,可反映各指标所包含信息的有序度及效能。采用熵权法确定各指标的权重,充分考虑了数据本身信息,可有效避免主观因素的影响,使指标权重更为客观合理[18],具体计算步骤如下:
(1)为消除各指标量纲的差异性,需将构建的样本空间矩阵R进行归一化处理,从而得到归一化后的判断矩阵B:
$$ {b_{ij}} = \frac{{{x_{ij}} - {x_{\min }}}}{{{x_{\max }} - {x_{\min }}}} $$ (4) 式中:xmax,xmin表示同指标下不同样本的最大值与最小值,故将各评价指标的实测值按上式计算得到判断矩阵B:
$$ {B} = \begin{array}{c} \;\;{\text{Cl}}^{\text{-1}}\begin{array}{cc}& \end{array}\begin{array}{c}\end{array}\text{TDS}\begin{array}{cc}& \end{array}\text{SAR}\begin{array}{cc}& \end{array}\text{A}\begin{array}{cc}& \end{array}\begin{array}{c}\end{array}\;\;\;\;\;{\text{SO}}_{\text{4}}{}^{2-} \\ \left[\begin{array}{ccccc}0.0243& 0.0561& 0.0804& 0.0117& 0.1502\\ 0.0373& 0.0725& 0.5867& 0.0143& 0.1709\\ 0.0039& 0.0087& 0.0104& 0.0048& 0.0158\\ 0.0010& 0.0043& 0.0129& 0.0014& 0.0082\\ 0.0151& 0.0523& 0.0780& 0.0030& 0.0809\\ 0.0147& 0.0352& 0.0432& 0.0112& 0.0680\\ 0.0087& 0.0206& 0.0172& 0.0066& 0.0395\\ 0.0204& 0.0385& 0.0139& 0.0059& 0.0240\\ \mathrm{...}& \mathrm{...}& \mathrm{...}& \mathrm{...}& \mathrm{...}\\ \text{0}\text{.0083 }& \text{0}\text{.0270 }& \text{0}\text{.0176 }& \text{0}\text{.0094 }& \text{0}\text{.0851 }\end{array}\right]\end{array} $$ (5) (2)依据熵的定义,由n个地下水样和m个指标可确定评价指标的熵为:
$$ {H_j} = - \frac{1}{{\ln n}}\left( {\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {{f_{ij}}\ln {f_{ij}}} } \right) $$ (6) $$ {f_{ij}} = \frac{{1 + {b_{ij}}}}{{\displaystyle\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^n {(1 + {b_{ij}})} }},i = 1,2, \cdots ,n;j = 1,2, \cdots ,m $$ (7) 由公式(6)和(7)计算得出各指标的熵值Hj:
$$ {H_j} = \left( {0.9970,0.9975,0.9970,0.9975,0.9979} \right)$$ (8) (3)计算评价指标的熵权W:
$$ W = {\left( {{w_j}} \right)_{1 \times m}} $$ (9) $$ {w}_{j}=\frac{1-{H}_{j}}{m-{\displaystyle {\sum }_{j=1}^{m}{H}_{j}}}\text{,}且{\displaystyle {\sum }_{j=1}^{m}{W}_{j}=1} $$ (10) 据实测数据与公式(9)和(10)计算各评价指标的权重wj,结果列于表5。
表 5 评价指标权重Tab. 5 The weights of evaluation indexes评价指标 Cl− TDS A SO42− SAR 权重 0.2311 0.1887 0.1907 0.1618 0.2277 2.1.4 计算属性测度与识别属性结果
属性测度是定量刻画第i个样本第j个指标值xij具有属性Ck的程度。据属性分类标准矩阵可知,文中aj1<aj2<···<ajk,则xij具有属性Ck的属性测度μijk=μ(xij∈Ck):
$$ \left\{ \begin{array}{l}若{x}_{ij} \lt {a}_{j1}\text{,}取{\mu }_{ij1}=1,{\mu }_{ij2}={\mu }_{ij3}= \cdots ={\mu }_{ijk}=0\\ 若{x}_{ij} \gt {a}_{jk}\text{,}取{\mu }_{ijk}=1,{\mu }_{ij1}={\mu }_{ij2}= \cdots ={\mu }_{ij(k-1)}=0\\ 若{a}_{jl} \lt {x}_{ij} \lt {a}_{j(l+1)}(k \lt l,或k \gt l+1)\text{,}\\ 取{\mu }_{ijl}=\dfrac{\left|{x}_{ij}-{a}_{j(l+1)}\right|}{\left|{a}_{jl}-{a}_{j(l+1)}\right|},{\mu }_{ij(l+1)}=\dfrac{\left|{x}_{ij}-{a}_{jl}\right|}{\left|{a}_{jl}-{a}_{j(l+1)}\right|},{\mu }_{ijk}=0\end{array} \right. $$ (11) 由式(11)可计算得到各水样单指标属性测度μijk,然后根据各指标权重wj,则可计算各水样的多指标综合属性测度μik:
$$ {\mu _{ik}} = \mu ({x_i} \in {{\text{C}}_k}){\text{ = }}\sum\nolimits_{j = 1}^m {{W_j}{\mu _{ijk}}\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {} \end{array}(1 \leqslant i \leqslant n,1 \leqslant k \leqslant K)} $$ (12) 按照置信度准则,置信度λ一般取0.6 ~ 0.75,本文取0.65计算ki:
$$ {k_i} = \min \left\{ {k:\sum\nolimits_{i = 1}^k {{\mu _{ki}} \geqslant \lambda ,1 \leqslant k \leqslant K} } \right\} $$ (13) 取k直到满足式(13),则认为xi属于Cki类。
按照属性识别的评分准则,计算海水入侵等级的特征值,等级特征值越大,海水入侵程度越低,计算公式为 :
$$ {q_{{x_i}}} = \sum\nolimits_{t = 1}^k {{n_t}{\mu _{xi}}({C_t})} $$ (14) 式中:qxi为海水入侵等级的特征值;nt=K+1−t,表示海水入侵等级属性集Ct的分值,随着t的增大,n t值递减。最终可依据qxi的大小对xi进行排序和比较。
利用式(11)和(12)计算出研究区各水样的属性测度μijk,式(13)确定了各水样的入侵等级Cki,式(14)计算得到了相应的入侵等级特征值qxi,并可根据该值对同一等级水样的入侵程度进行排序和比较,计算结果见表6。由分析结果可知,熵权属性识别法不仅能客观地评价海水入侵等级,还可以比较同等级水样的入侵程度。海水入侵等级特征值越小,入侵程度越高,如F-02与F-27的水样虽同属于Ⅱ级,但F-02的特征值小于F-27,故可判断F-02比F-27的入侵程度相对略高,分析原因主要在于二者的SAR值存在较大差异(表3),F-02的SAR值为24.64,而F-27的SAR值为1.86,即F-02的Na+相对比值高于F-27,表征F-02的阳离子交替吸附作用强于F-27,入侵区地下水中Ca2+和Mg2+逐渐被Na+取代,故评价结果科学合理。
表 6 属性测度及海水入侵等级评价结果Tab. 6 Attribute measurement and evaluation results of seawater intrusion level水样
编号属性测度 特征值 评价
等级水样
编号属性测度 特征值 评价
等级Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ qxi Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ qxi F-01 0.33 0.60 0.07 2.254 Ⅱ S-01 0.68 0.15 0.17 2.508 Ⅰ F-02 0.25 0.42 0.33 1.916 Ⅱ S-02 0.71 0.29 0.00 2.709 Ⅰ F-03 0.85 0.15 0.00 2.850 Ⅰ S-03 0.41 0.41 0.18 2.227 Ⅱ F-05 0.96 0.04 0.00 2.962 Ⅰ S-05 0.24 0.52 0.25 1.994 Ⅱ F-06 0.75 0.25 0.00 2.747 Ⅰ S-06 0.69 0.18 0.14 2.547 Ⅰ F-07 0.61 0.35 0.04 2.563 Ⅱ S-08 0.88 0.12 0.00 2.877 Ⅰ F-08 0.77 0.23 0.00 2.767 Ⅰ S-09 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.000 Ⅲ F-09 0.74 0.26 0.00 2.737 Ⅰ S-10 0.41 0.40 0.19 2.215 Ⅱ F-10 0.68 0.16 0.16 2.521 Ⅰ S-11 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.000 Ⅲ F-12 0.72 0.24 0.03 2.693 Ⅰ S-12 0.62 0.25 0.14 2.479 Ⅱ F-13 0.64 0.35 0.01 2.633 Ⅱ S-13 0.67 0.16 0.16 2.506 Ⅰ F-14 0.49 0.43 0.07 2.420 Ⅱ S-16 0.56 0.28 0.17 2.392 Ⅱ F-16 0.26 0.56 0.18 2.087 Ⅱ S-17 0.59 0.22 0.19 2.396 Ⅱ F-17 0.95 0.05 0.00 2.954 Ⅰ S-18 0.42 0.37 0.21 2.218 Ⅱ F-18 0.49 0.42 0.08 2.413 Ⅱ S-19 0.68 0.13 0.19 2.490 Ⅰ F-19 0.30 0.61 0.08 2.219 Ⅱ S-20 0.71 0.12 0.17 2.545 Ⅰ F-20 0.29 0.45 0.26 2.030 Ⅱ S-21 0.90 0.10 0.00 2.901 Ⅰ F-21 0.84 0.16 0.00 2.839 Ⅰ S-22 0.89 0.11 0.00 2.890 Ⅰ F-22 0.61 0.21 0.18 2.428 Ⅱ S-23 0.64 0.17 0.19 2.445 Ⅱ F-25 0.51 0.31 0.17 2.339 Ⅱ S-24 0.77 0.12 0.11 2.664 Ⅰ F-26 0.82 0.18 0.00 2.818 Ⅰ S-25 0.65 0.16 0.19 2.460 Ⅰ F-27 0.55 0.32 0.13 2.429 Ⅱ S-26 0.75 0.18 0.08 2.668 Ⅰ F-29 0.31 0.46 0.23 2.082 Ⅱ S-28 0.71 0.22 0.07 2.644 Ⅰ F-30 0.75 0.10 0.15 2.594 Ⅰ S-29 0.78 0.20 0.02 2.768 Ⅰ F-31 0.99 0.01 0.00 2.986 Ⅰ S-30 0.68 0.29 0.03 2.654 Ⅰ 2.2 评价结果对比分析
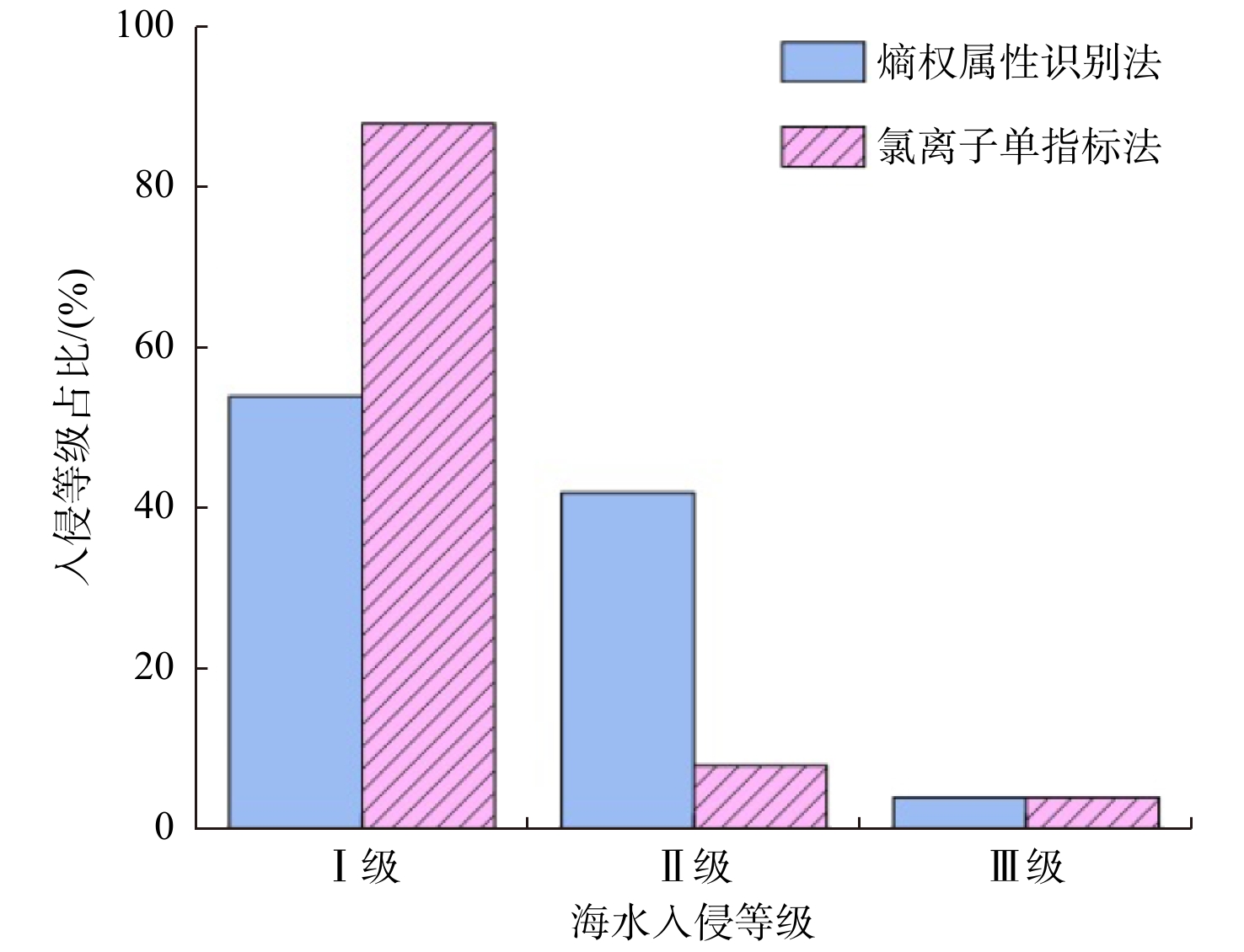
为验证熵权属性识别法评价结果的有效性,将其与《海水入侵监测与评价技术规程》(HY/T 0314-2021)推荐的氯离子单指标法结果进行了对比(图3)。结果显示,熵权属性识别法和氯离子单指标法判别为无入侵水样的占比分别为54%和88%,轻度入侵水样的占比分别为42%和8%,严重入侵水样的占比均为4%。经分析,两种方法评价结果的一致性达66%,其中严重入侵等级结果完全一致,而轻度入侵和无入侵等级结果存在差异,相对而言,熵权属性识别法评价的入侵等级较高,34%的水样被氯离子单指标法判别为Ⅰ级,而被熵权属性识别法划分为Ⅱ级。进一步分析可知,虽然评价结果不一致的水样的Cl−浓度没有超过Ⅰ级标准(250 mg/L),但其SAR值或者A值已经达到轻度入侵程度(SAR>2或A>1),如F-01、F-07以及S-03等,个别水样甚至达到了严重入侵程度(SAR>6.7 或A>3.6),如F-02和S-17,表明这些水样已经不同程度地受到阳离子交替吸附作用或者咸淡水混合作用的影响,体现出咸淡水过渡带的典型特征,这说明熵权属性识别法客观全面地利用了各评价样本信息,评价结果更加准确可靠。
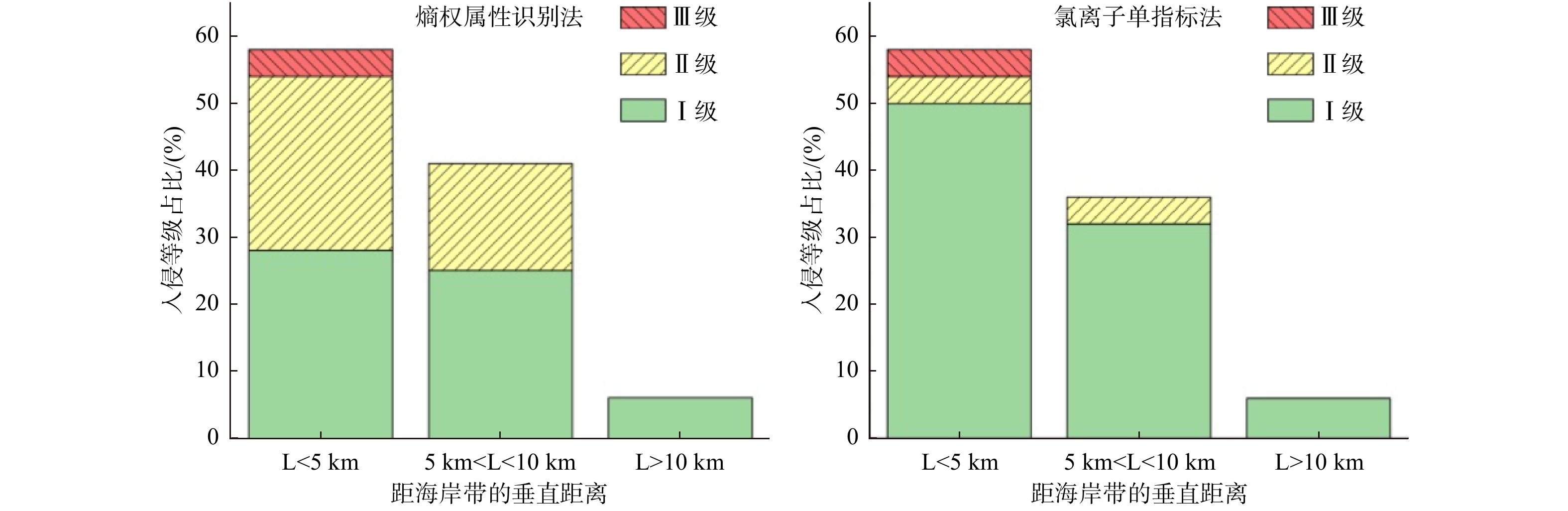
根据熵权属性识别法计算得到的各水样海水入侵等级特征值qxi以及氯离子单指标法的Cl−浓度值,分别绘制了相应的研究区海水入侵分布图(图4和图5)。经分析可知,两种方法评价的严重海水入侵区一致,均分布在周家窝铺−庆屯−海套村一带,主要为距海岸带垂直距离小于5 km的海水养殖区,且属地下水位负值区(图1、图6),故可推断地下水超采、海水养殖等人为活动加剧了该区域海水入侵程度,使地下水呈严重入侵特征。两种评价方法所得到的轻度入侵区在黑泥坑−中兴−庙后头村一带和狐狸套−王家河子村一带均有分布,该类地区多分布于距海岸带垂直距离小于10 km的范围内(图6),主要受人为开采影响,形成了地下水位负值区(图1),使得海水沿松散孔隙含水层向内陆入侵;此外,熵权属性识别法评价结果中,轻度入侵区除以上区域外,还包括烟台河、东沙河以及兴城河的河口地段,这不仅与实地调查结果一致,也与文献[19-20]中兴城河−烟台河海水入侵区分布的结论吻合,河口地段入侵主要受海洋潮汐作用以及河道采砂影响,引发了海水沿河道上溯浸染。
综上所述,两种方法的评价结果具有较一致的对应关系,而且熵权属性识别法的结果与实际的海水入侵分布更相符,研究区以轻度入侵为主,局部地段存在严重入侵,说明兴城市的海水入侵灾害是过量开采地下水、海水养殖、河道采砂以及河口上溯等多因素共同作用的结果,但不同入侵区的主导因素有所差异,入侵区地下水化学成分变化由咸淡水的机械混合作用、阳离子交替吸附作用以及人为活动等综合作用所致。
3 结 论
(1)将熵权属性识别法应用于兴城市海水入侵程度评价,选取了5项表征海水入侵程度的地下水化学因子作为评价指标,经计算,各评价指标的权重从大到小依次为Cl−、SAR、A、TDS、SO42−。该方法充分利用了实测样本信息,考虑了各个样本数据间的联系,有效降低了确定评价指标权重的主观性,同时可根据评价结果对同一入侵等级的水样进行比较和排序,相比氯离子单指标法,评价结果更加准确可靠。
(2)结果表明,研究区以轻度入侵为主,局部存在严重入侵,42%的采样点为轻度入侵,4%的采样点为严重入侵;轻度入侵区主要分布于距海岸带10 km内的地下水位负值区,集中分布在黑泥坑−中兴−庙后头村一带、狐狸套−王家河子村一带以及烟台河、东沙河以及兴城河的河口地段;严重入侵区主要分布于距海岸带5 km内的地下水位负值区与海水养殖区,集中分布在周家窝铺−庆屯−海套村一带。
-
表 1 地下水样品水化学特征的统计表(N=50)
Tab. 1 Statistics table of water chemical characteristics of groundwater samples (N=50)
测试指标 最小值/mg·L−1 最大值/mg·L−1 平均值/mg·L−1 标准差/mg·L−1 变异系数 TDS 177.00 11532.90 894.46 1830.10 2.05 Na+ 19.66 2793.31 164.18 441.97 2.69 Mg2+ 10.58 272.33 35.52 44.23 1.25 Ca2+ 25.98 737.28 111.19 105.33 0.95 Cl− 17.96 6369.00 392.17 1242.08 3.17 SO42− 17.81 1196.00 140.66 195.49 1.39 HCO3− 52.46 761.28 167.25 124.34 0.74 表 2 评价指标的选取依据
Tab. 2 Selection basis of evaluation indexes
评价指标 确定依据 Cl− 地下水中最稳定的离子,为判别海水入侵最敏感的指标 TDS 地下水各种离子、分子、化合物的总量(除悬浮物外),能直接体现海水与地下淡水之间的差异 SO42− 海水中较稳定的离子,地下淡水中含量较少,地下水受海水侵染后变化较敏感的指标 A 咸化系数${\text{A} } = { {\gamma ({\text{C} }{ {\text{l} }^{^\_} })}/{[\gamma ({\text{HCO} }_3^{^\_}) + \gamma ({\text{CO} }_{\text{3} }^{ { {\text{2} }^{\text{\_} } } })]} }$,其中:Cl−和HCO3−(CO32−)分别为海水与地下淡水的主要阴离子,二者比值可有效区分滨海地区的地下水类型;A是从阴离子角度分析海水入侵的程度,可反映咸淡水混合作用的强弱 SAR 钠吸附比${\text{SAR} } = { {\gamma ({\text{N} }{ {\text{a} }^ + })}/{\sqrt {0.5\gamma ({\text{C} }{ {\text{a} }^{2 + } }) + 0.5\gamma ({\text{M} }{ {\text{g} }^{2 + } })} } }$,其中:Na+是海水中首要的阳离子,其含量比地下淡水高出2~4个数量级;Ca2+和Mg2+是地下淡水中主要阳离子;SAR是从阳离子角度分析海水入侵的程度,可表征阳离子交替吸附作用的强弱 注:γ为毫克当量浓度 表 3 研究区海水入侵程度评价样本的空间矩阵
Tab. 3 Spatial matrix of seawater intrusion evaluation samples in the study area
编号 Cl−
/mg·L−1TDS
/mg·L−1SAR A SO42−
/mg·L−1编号 Cl−
/mg·L−1TDS
/mg·L−1SAR A SO42−
/mg·L−1F-01 144.53 492 2.07 1.26 186.53 S-01 64.20 362 1.16 0.96 102.81 F-02 215.56 519 24.64 1.50 211.12 S-02 23.11 526 1.73 0.43 121.72 F-03 33.35 177 1.15 0.63 26.85 S-03 130.12 1150 1.26 1.20 209.46 F-05 17.96 138 1.50 0.31 17.81 S-05 275.86 1090 2.80 4.86 160.75 F-07 105.04 380 1.48 1.21 88.87 S-08 33.41 200 1.31 0.52 28.39 F-17 28.06 191 1.03 0.33 60.09 S-09 6369.00 11532 31.47 183.33 1196.00 F-21 34.90 199 0.85 0.62 62.55 S-10 253.86 936 1.27 4.71 131.02 F-22 77.21 341 2.27 0.87 65.29 S-11 5479.53 4450 9.50 58.11 697.51 F-27 136.36 442 1.86 1.48 84.26 S-17 148.99 473 2.25 4.89 40.39 表 4 海水入侵评价指标的分级标准及代表值
Tab. 4 Classification criteria and representative values of seawater intrusion evaluation indexes
评价指标 无入侵Ⅰ级 轻度入侵Ⅱ级 严重入侵Ⅲ级 等级范围 代表值 等级范围 代表值 等级范围 代表值 Cl−/mg·L−1 <250 100 250~1000 500 >1000 1500 TDS/mg·L−1 <1000 500 1000~3000 1500 >3000 4500 A <1.0 0.5 1.0~3.6 1.5 >3.6 5.7 SO4−/mg·L−1 <100 50 100~300 150 >300 450 SAR <2.0 1.0 2.0~6.7 3.0 >6.7 10.0 表 5 评价指标权重
Tab. 5 The weights of evaluation indexes
评价指标 Cl− TDS A SO42− SAR 权重 0.2311 0.1887 0.1907 0.1618 0.2277 表 6 属性测度及海水入侵等级评价结果
Tab. 6 Attribute measurement and evaluation results of seawater intrusion level
水样
编号属性测度 特征值 评价
等级水样
编号属性测度 特征值 评价
等级Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ qxi Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ qxi F-01 0.33 0.60 0.07 2.254 Ⅱ S-01 0.68 0.15 0.17 2.508 Ⅰ F-02 0.25 0.42 0.33 1.916 Ⅱ S-02 0.71 0.29 0.00 2.709 Ⅰ F-03 0.85 0.15 0.00 2.850 Ⅰ S-03 0.41 0.41 0.18 2.227 Ⅱ F-05 0.96 0.04 0.00 2.962 Ⅰ S-05 0.24 0.52 0.25 1.994 Ⅱ F-06 0.75 0.25 0.00 2.747 Ⅰ S-06 0.69 0.18 0.14 2.547 Ⅰ F-07 0.61 0.35 0.04 2.563 Ⅱ S-08 0.88 0.12 0.00 2.877 Ⅰ F-08 0.77 0.23 0.00 2.767 Ⅰ S-09 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.000 Ⅲ F-09 0.74 0.26 0.00 2.737 Ⅰ S-10 0.41 0.40 0.19 2.215 Ⅱ F-10 0.68 0.16 0.16 2.521 Ⅰ S-11 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.000 Ⅲ F-12 0.72 0.24 0.03 2.693 Ⅰ S-12 0.62 0.25 0.14 2.479 Ⅱ F-13 0.64 0.35 0.01 2.633 Ⅱ S-13 0.67 0.16 0.16 2.506 Ⅰ F-14 0.49 0.43 0.07 2.420 Ⅱ S-16 0.56 0.28 0.17 2.392 Ⅱ F-16 0.26 0.56 0.18 2.087 Ⅱ S-17 0.59 0.22 0.19 2.396 Ⅱ F-17 0.95 0.05 0.00 2.954 Ⅰ S-18 0.42 0.37 0.21 2.218 Ⅱ F-18 0.49 0.42 0.08 2.413 Ⅱ S-19 0.68 0.13 0.19 2.490 Ⅰ F-19 0.30 0.61 0.08 2.219 Ⅱ S-20 0.71 0.12 0.17 2.545 Ⅰ F-20 0.29 0.45 0.26 2.030 Ⅱ S-21 0.90 0.10 0.00 2.901 Ⅰ F-21 0.84 0.16 0.00 2.839 Ⅰ S-22 0.89 0.11 0.00 2.890 Ⅰ F-22 0.61 0.21 0.18 2.428 Ⅱ S-23 0.64 0.17 0.19 2.445 Ⅱ F-25 0.51 0.31 0.17 2.339 Ⅱ S-24 0.77 0.12 0.11 2.664 Ⅰ F-26 0.82 0.18 0.00 2.818 Ⅰ S-25 0.65 0.16 0.19 2.460 Ⅰ F-27 0.55 0.32 0.13 2.429 Ⅱ S-26 0.75 0.18 0.08 2.668 Ⅰ F-29 0.31 0.46 0.23 2.082 Ⅱ S-28 0.71 0.22 0.07 2.644 Ⅰ F-30 0.75 0.10 0.15 2.594 Ⅰ S-29 0.78 0.20 0.02 2.768 Ⅰ F-31 0.99 0.01 0.00 2.986 Ⅰ S-30 0.68 0.29 0.03 2.654 Ⅰ -
[1] 杨桂山. 中国沿海海水入侵机制和变化规律的初步研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 1993, 2(2): 75-82. [2] 黄 磊, 郭占荣. 中国沿海地区海水入侵机理及防治措施研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2008, 19(2): 118-123. [3] ZENG X K, WU J C, WANG D, et al. Assessing the pollution risk of a groundwater source field at western Laizhou Bay under seawater intrusion[J]. Environmental Research, 2016, 148: 586-594. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2015.11.022
[4] 熊贵耀, 付腾飞, 徐兴永, 等. 滨海含水层海水入侵影响因素研究综述[J]. 海洋科学, 2019, 43(6): 102-112. doi: 10.11759/hykx20181105001 [5] ABD-ELHAMID H, ABDELATY I, SHERIF M. Evaluation of potential impact of Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam on Seawater Intrusion in the Nile Delta Aquifer[J]. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 16(5): 2321-2332. doi: 10.1007/s13762-018-1851-3
[6] PÉREZ-MARTÍN M A, ESTRELA T, ANDREU J, et al. Modeling water resources and river-aquifer interaction in the Júcar River Basin, Spain[J]. Water Resources Management, 2014, 28(12): 4337-4358. doi: 10.1007/s11269-014-0755-3
[7] 崔 震, 陈广泉, 徐兴永, 等. 北长山岛海水入侵成因机理及现状评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2015, 34(6): 930-936. [8] 刘 莹, 姜锡仁, 王 兴, 等. 莱州湾南岸海水入侵变化趋势及成因分析[J]. 海洋科学, 2018, 42(2): 108-117. doi: 10.11759/hykx20170111002 [9] 虞未江, 贾 超, 狄胜同, 等. 基于模糊数学和改进层次分析法的海水入侵程度评价[J]. 海洋科学, 2018, 42(6): 19-29. [10] 房 琦, 范 尧, 程 鹏, 等. 单因子界定联合模糊综合评判的海水入侵评价方法——以日照两城河地下水海水入侵现状评价为例[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2017, 24(5): 9-14. [11] 涂向阳, 高学平. 模糊数学在海水入侵地下水水质评价中的应用[J]. 水利学报, 2003, 34(8): 64-69. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2003.08.013 [12] 章 斌, 宋献方, 韩冬梅, 等. 运用数理统计和模糊数学评价秦皇岛洋戴河平原的海水入侵程度[J]. 地理科学, 2013, 33(3): 342-348. [13] 孙振宇, 宋献方, 卜红梅, 等. 秦皇岛洋河-戴河流域浅层地下水咸化程度评价[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2015, 15(3): 356-361. [14] 刚什婷, 贾 涛, 王宝春, 等. 基于熵权法的集对分析模型在青岛市崂山区海水入侵现状评价中的应用[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2019, 38(6): 939-944,976. doi: 10.12111/j.mes20190618 [15] 李 淼, 夏 军, 李福林, 等. 基于熵权的属性识别模型在海水入侵现状评价中的应用[J]. 地理科学进展, 2012, 31(3): 324-329. [16] 王 鼐, 董维红, 张 岩, 等. 开封南郊垃圾场地下水质量的熵权属性识别评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2012, 39(2): 94-99. [17] 杨春玲. 基于属性数学的综合评价模型[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2008. [18] 薛剑光, 周 健, 史秀志, 等. 基于熵权属性识别模型的岩体可爆性分级评价[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 41(1): 251-256. [19] 李 慧. 葫芦岛地区海水入侵区的成因及规律分析[J]. 吉林水利, 2010 (2): 9-10,19. [20] 姜嘉礼. 葫芦岛市滨海地区海水入侵研究[J]. 水文, 2002, 22(2): 27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2002.02.007 -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 阳建新,张龙济,孙金鹏,高晓立,曹湘悦,林国庆,李发菊. 基于熵权属性识别模型的唐山海咸水入侵评价. 海洋湖沼通报. 2024(02): 109-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张耀文,李海君,赵倩,贾进军,王贺. 兴城市典型海水入侵区水文地球化学特征. 海洋地质前沿. 2024(08): 32-41 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王颖. 基于层次分析法的海水入侵评价研究及应用. 水资源开发与管理. 2024(10): 58-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王颖. 灰色关联分析法在海水入侵水质评价中的应用. 水资源开发与管理. 2024(11): 69-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘倩. 锦州市海水入侵综合评价. 黑龙江水利科技. 2024(12): 171-175 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载: