Responses of distribution of water quality in the Sansha bay on the land discharge and aquaculture
-
摘要:
根据福建三沙湾海域2018年洪季一个定点站和12个走航站的5项营养盐及水文资料,研究发现:(1)三沙湾沿岸城市排放水是主要的污染源。其中,蕉城区外大金溪湾的硝酸盐、氨盐、悬沙含量、硅酸盐和磷酸盐浓度,在落潮盐度最小时期(宁德城区排放水)分别是涨潮盐度最大时期(海水)水质浓度的1.2倍、3.6倍、6倍、2.5倍和2倍。(2)三沙湾营养盐从陆向海的变化既受陆域河流排放的影响,也受湾内养殖排放的影响。其中NO3-N和SiO3-Si浓度受陆源排放影响较大,从陆向海分别下降了31%和50%。而NO2-N、NH4-N和PO4-P浓度变化受湾内养殖的影响,从陆向海下降的趋势不明显。(3)12个走航站无机氮(DIN)的平均值为57.33 μmol/L,大于21.41 μmol/L;PO4-P平均值为2.28 μmol/L,大于1.45 μmol/L;DIN/DIP基本为8~30。这些参数表明三沙湾水质已经超四类海水水质标准,并达到富营养化状态。
Abstract:Based on nutrients and hydrological data of one fixed station and twelve navigation stations in 2018 flood season in the Sansha bay, Fujian province, this paper found: (1) The average concentrations of SiO3-Si、NO3-N、NH4-N、PO4-P and SSC in ebb (includes drainage of the Ningde city) are about 1.2, 3.6, 6, 2.5 and 2 times higher than that in the flood (seawater) in Dajinxi estuary, respectively. (2)The concentrations of NO3-N and SiO3-Si decrease by 31% and 50% with the increased of salinity, the result indicated SiO3-Si and NO3-N variation were controlled by river discharge. However, with increase of salinity, the concentrations of NH4-N and PO4-P showed a slight decrease trend, and NO2-N even showed an increase trend, the result implicated that change of NH4-N、PO4-P and NO2-N were mainly controlled by aquaculture in the bay. (3) The average concentrations of inorganic nitrogen (DIN) on twelve navigation stations was 57.33>21.41 μmol/L, PO4-P (DIP) was 2.28>1.45 μmol/L, and DIN/DIP was between 8~30, such level of above parameters indicated that the water quality in the Sansha bay had exceeded the grade IV water quality standard and reached the state of eutrophication.
-
Keywords:
- the Sansha bay /
- nutrients /
- land discharge /
- aquaculture /
- human activities
-
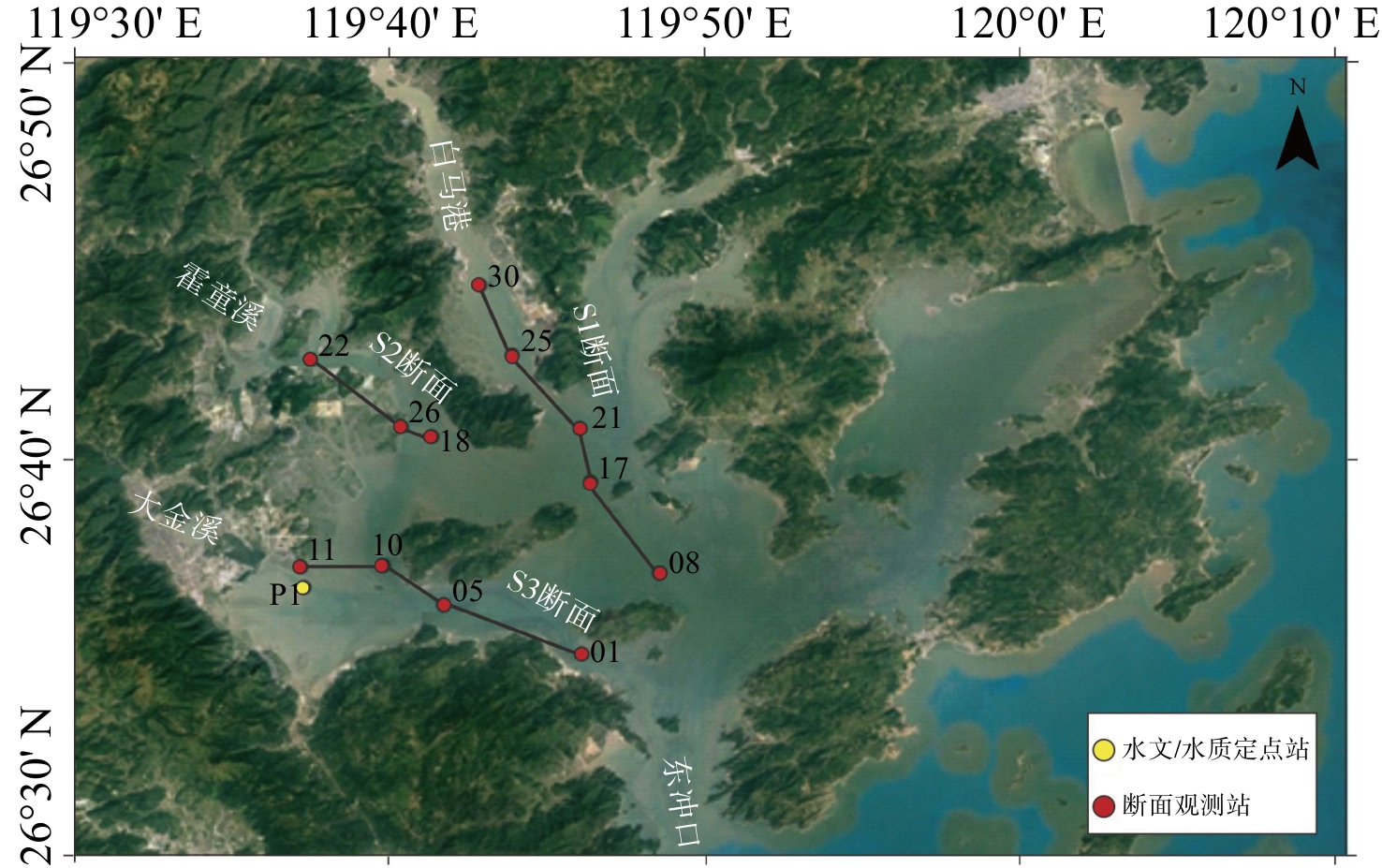
三沙湾位于福建省宁德市,是东冲半岛和鉴江半岛围合而成的近封闭型海湾,周边人口200多万,海域面积570 km2,水域辽阔[1],年平均气温17 ℃~19 ℃,年均水温约为20.3 ℃,年均盐度约为27。因其避风、水深且水质好而成为重要的养殖区域,2010年鱼、虾、贝等水产品总产量达29.7万吨,2012年湾内养殖网箱达20多万个,是我国最大的海水人工繁育和网箱养殖基地,该海域的养殖产业已经成为闽东海洋经济的支柱产业[2]。随着陆源污染和湾内养殖的迅速发展,三沙湾的水质污染及其养殖灾害不断加剧。据资料统计,无机氮、活性磷酸盐的浓度2012年和2013年分别是1991年的3.8倍和6.7倍[3-4],均超过三类海水水质标准。湾内养殖的增加使叶绿素a的含量2000年比1990年增加了2.05倍,赤潮自2004年以来至少发生14起,成灾面积达312 km2 [5-6],这导致湾内养殖灾害的频率和规模也在不断增加。由于过量营养盐(氮、磷)的输入,导致水体交换不畅的港湾易发生富营养化,这将制约经济的可持续发展,并威胁到人类的健康[7]。实际上,全球都面临着近海和海湾的富营养化问题,而且富营养化的动力因素极其复杂[8-10]。研究表明,陆源污染、养殖、全球气候变暖、洋流和沿岸流等因素都对富营养化过程有重要影响[11-15]。对于三沙湾而言,因养殖规模巨大,其富营养化过程不仅与周边河流的输入有关,还与湾内养殖有密切的关系。以前的研究多侧重于流域输入对湾内水质的影响[16-17],而关于养殖对湾内水质影响的研究尚不足。尽管有些研究已注意到湾内养殖对水质的影响,但多侧重于某一具体的养殖区域[11, 18-20],对于流域输入和湾内养殖双重因素对湾内水质变化的贡献和作用的研究更是不充分的。人们并不清楚三沙湾水质变化与陆源污染和湾内养殖的具体关系,这一现状严重影响了水质治理的效率和对水质污染进行有针对性的治理。针对上述目标,在三沙湾宁德城区外侧的大金溪河口布设一个定点站位,观测水质的潮汐变化过程,分析陆源输入(城区排放)对湾内水质的影响;另外从陆向海布设交溪白马港、霍童溪和大金溪3个断面12个走航站(见图1),观测水质从陆向海的变化,分析陆源输入和湾内养殖对水质分布的影响,为有效控制养殖区水体富营养化提供科学依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1 调查方式
2018年6月22日至29日,在大金溪河口P1站位做连续观测(定点调查,小渔船),每小时取一次水样,同时利用声学多普勒流速剖面仪(ADCP,600 kHZ)观测水深、流速和流向;利用光学后向散射浊度仪(OBS-3A)观测悬沙浊度和盐度。走航调查利用“闽平渔63333”船,分别在3个断面(S1、S2、S3)12个站位采集水质样品带回实验室,利用多参数营养盐分析仪分析5项营养盐,同时也利用OBS-3A观测每个站点悬沙浊度和盐度(见图1)。其中,S1长21 km,S2长11 km,S3长19 km。另外,在现场同步采集悬沙水样,带回实验室标定悬沙浊度-悬沙含量曲线,将悬沙浊度换算成悬沙含量(SSC)。
1.2 样品采集及分析方法
水体样品的采集、贮存和处理方法均按照《海洋监测规范 》[21]进行。前处理:购买50 mL聚乙烯塑料瓶,用10% HNO3浸泡3 d,再用蒸馏水冲洗干净。采样:采集湾内表层水样,先用少量过滤(60 mL注射器+whatman,GF/F膜过滤)后的水样荡洗50 mL聚乙烯瓶,然后装入过滤水样,再加入1 mL氯化汞,盖好瓶塞,振摇1 min后放低温冰箱内保存。下船后,将样品装入保温箱快递到华东师范大学实验室。分析:带回实验室后用多元素分析仪器测定5项营养盐[硝酸盐(NO3-N)、亚硝酸盐(NO2-N)、氨盐(NH4-N)、活性硅酸盐(SiO3-Si)、活性磷酸盐(PO4-P)]。其中,5项营养盐的测定利用荷兰Skalar公司的连续流动分析仪(San plus)测定样品,NO3-N采用Cd-Cu还原法,NO2-N采用重氮偶氮比色法,NH4-N采用靛酚蓝法,PO4-P采用磷钼蓝法,SiO3-Si采用硅钼蓝法,实验用水均为Milli-Q水,实验过程中实施质量控制,分析误差小于5%。实验室5项营养盐分析的仪器、流程和质量控制均通过国家质量认定(http://www.sklec.ecnu.edu.cn/AboutUs/CMA)。
1.3 水质和富营养化评价方法
水质采用《海水水质标准》(GB 3097-1997)[22]评价。一类海水:无机氮(DIN)≤0.20 mg/L (14.28 μmol/L),活性磷酸盐 (PO4-P) ≤ 0.015 mg/L(0.484 μmol/L);二类海水:无机氮≤0.30 mg/L(21.42 μmol/L),活性磷酸盐≤0.03 mg/L (0.97 μmol/L);三类海水:无机氮≤0.40 mg/L(28.57 μmol/L),活性磷酸盐≤0.03 mg/L (0.97 μmol/L);四类海水:无机氮≤0.50 mg/L(35.7 μmol/L),活性磷酸盐≤0.045 mg/L (1.45 μmol/L)。其中,无机氮含量为NH4-N、NO3-N、NO2-N之和。
当前水域营养级评价方法主要有单项指标评价法、综合指数评价法和模糊数学评价法[16, 23-25],这些模式虽然各有其合理性的一面,但都未能揭示出营养盐限制对富营养化的影响。本文采用郭卫东的综合营养级方法作为三沙湾水域富营养化的评价标准,该方法以潜在富营养化的概念为基础,适用于大部分水体[26]。实际上,水域富营养化的评价需要符合浮游植物的正常生长要求,将对浮游生物起限制性作用的氮、磷作为评价参数,同时参照海水水质标准。该方法根据氮、磷浓度将水体划分为贫营养水质(DIN<14.28 μmol/L,PO4-P<0.97 μmol/L),富营养水质(DIN>21.41 μmol/L, PO4-P>1.45 μmol/L)和中度营养水质(氮、磷浓度介于两者之间)。当DIN/DIP>30时,为磷限制;当DIN/DIP<8时,为氮限制(见表1)。
表 1 水域营养级综合评价标准Tab. 1 Classification of nutrient levels等级 富养级 DIN/μmol·L−1 PO4-P/μmol·L−1 N:P I 贫营养 <14.28 <0.97 8~30 II 中度营养 14.28~21.41 0.97~1.45 8~30 III 富营养 >21.41 >1.45 8~30 IVP 磷限制中度营养 14.28~21.41 >30 VP 磷中等限制潜在性富营养 >21.41 30~60 VIP 磷限制潜在性富营养 >21.41 >60 IVN 氮限制中度营养 0.97~1.45 <8 VN 氮中等限制潜在性富营养 >1.45 4~8 VIN 氮限制潜在性富营养 >1.45 <4 2 结果与讨论
2.1 三沙湾营养盐的时空变化特征
2.1.1 营养盐的潮汐变化特征
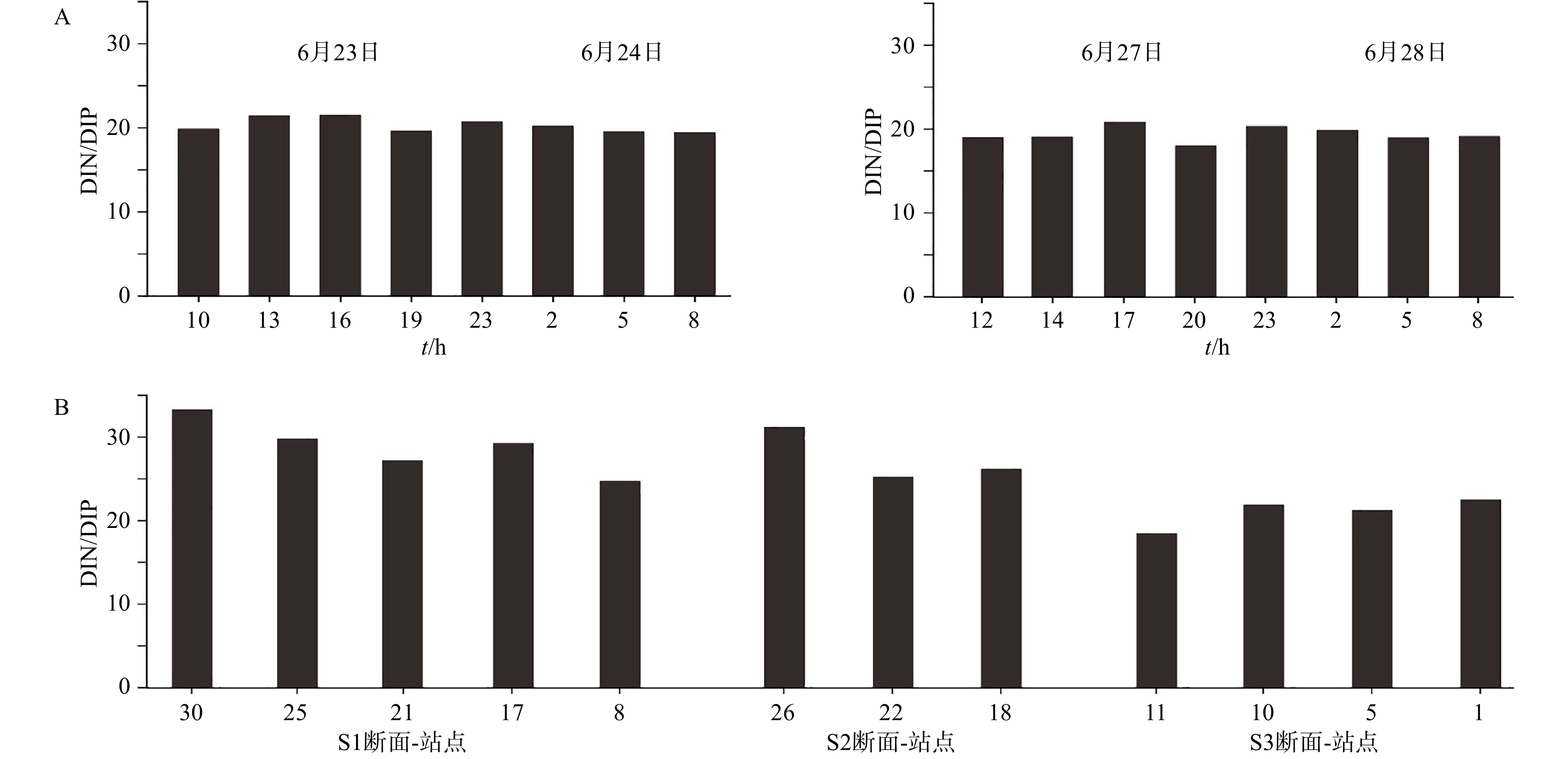
定点站P1涨、落潮的潮差、流速均没有显著差异。小潮涨、落潮潮差分别为5.0 m和4.8 m,平均流速分别为9.4 cm/s和12.0 cm/s;大潮涨、落潮潮差分别为6.1 m和4.8 m,平均流速分别为12.8 cm/s和10.2 cm/s;大、小潮的潮差和流速在涨、落潮中没有明显差异(图2A、图2B)。
涨、落潮的营养盐和悬沙含量(SSC)随盐度变化呈现显著差异。落潮营养盐浓度随盐度减小不断增加,涨潮营养盐浓度随盐度增加不断降低。小潮涨落潮过程中,盐度从27减少到21 ; NO3-N、NH4-N、SSC、SiO3-Si和PO4-P分别从37.7 μmol/L増至 44.3 μmol/L、35.4 μmol/L増至128 μmol/L、 0.02 g/L増至0.12 g/L、55.5 μmol/L増至136.2 μmol/L、4.17 μmol/L増至8.45 μmol/L,其最大值分别为最小值的1.2倍、3.6倍、6倍、2.5倍和2倍( 见图2C、图2D、图2E);其中,NH4-N的浓度总体上显著大于NO3-N浓度。大潮营养盐浓度的涨、落潮变化与小潮过程类似,变化幅度相近(见图2C、图2D、图2E)。
2.1.2 营养盐空间分布
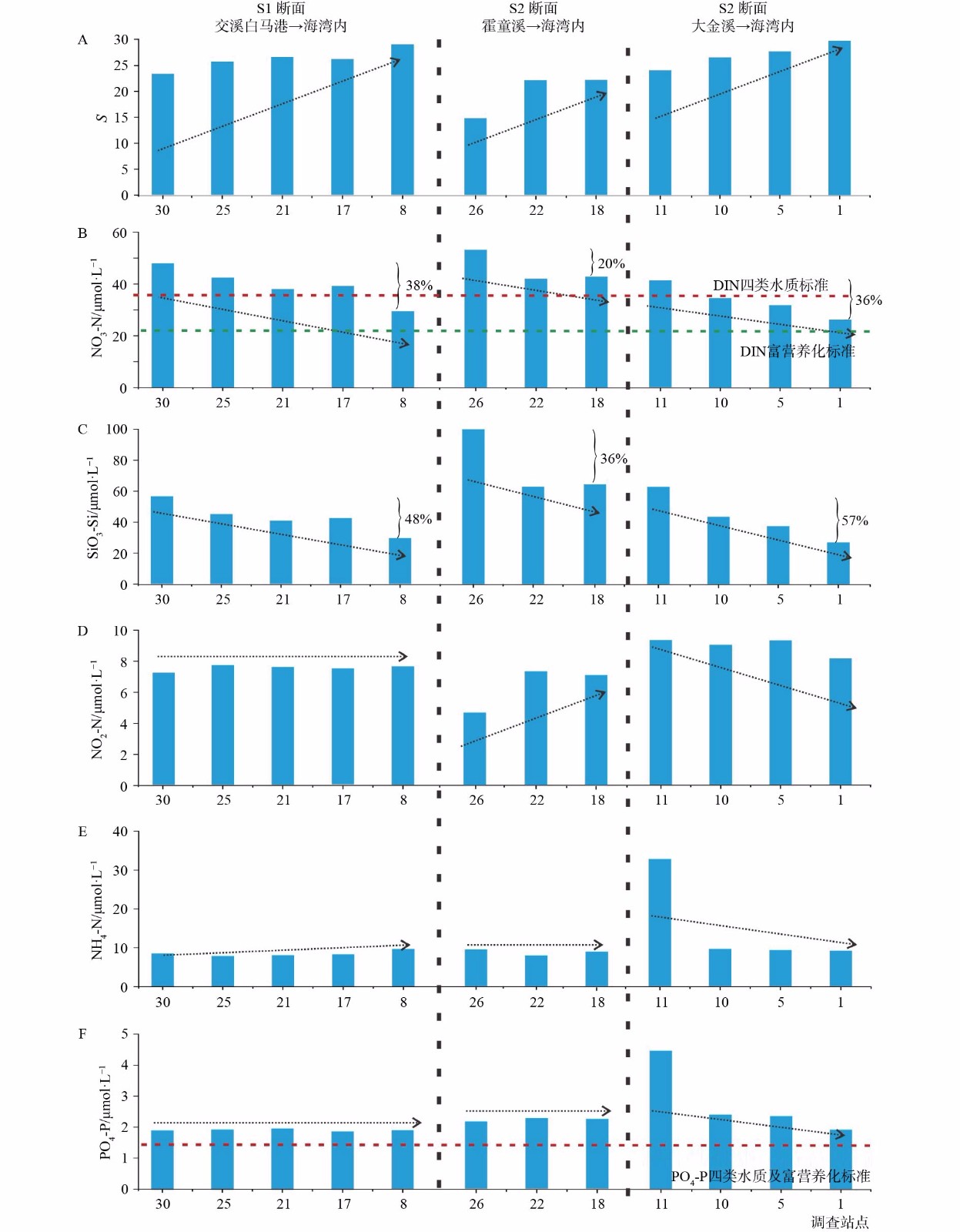
3个断面12个走航站从陆向海水质参数有显著性差异。NO3-N和SiO3-Si浓度从陆向海随盐度增加显著下降。其中,盐度沿S1、S2和S3断面分别由23.3增加到28.9、14.6增加到21.9 、23.9增加到29.6,其梯度分别为0.26、0.66和0.3 (μmol/L)(见图3A);NO3-N浓度沿S1、S2和S3断面随盐度增加分别由47.9 μmol/L下降到29.5 μmol/L、52.7 μmol/L下降到42.4 μmol/L、41.1 μmol/L下降到26.2 μmol/L,降幅分别为38%、20% 和36%,平均下降31%;盐度变化梯度分别为3.3、1.4和2.6(见图3B);SiO3-Si在3个断面分别由56.2 μmol/L下降到29.1 μmol/L、99.4 μmol/L下降到64.0 μmol/L、62.2 μmol/L下降到26.5 μmol/L,下降幅度分别为48%、36%和57%,平均下降50%;盐度变化梯度分别为4.8、5.1和6.3(见图3C)。NO2-N、NH4-N和PO4-P浓度从陆向海随盐度增加而下降的趋势不明显。其中,NO2-N在S1和S3断面呈现略微减少的趋势,但在S2断面上却由4.65 μmol/L增加到7.07 μmol/L(见图3D);NH4-N在S1断面呈现稍微增加的趋势,在S2和S3断面基本稳定(除去S3断面大金溪河口11站,其NH4-N浓度基本与NO3-N浓度相等)(见图3E)。PO4-P在3个断面基本稳定(除去S3断面大金溪河口11站)(见图3F)。
2.2 水质和富营养水平
定点站P1大、小潮DIN范围为58.09~154.31 μmol/L,平均值为82.21 μmol/L;PO4-P范围为2.86~8.45 μmol/L,平均值为4.70 μmol/L。DIN和DIP均超过四类海水水质标准和富营养化标准(见图2D、图2E)。12个走航站DIN范围为43.37~83.01,平均值为57.33;PO4-P的范围为1.87~4.48,平均值为2.28,DIN和DIP均超过四类海水水质标准和富营养化标准(见图3B、图3F)。故三沙湾水质超过四类海水水质,已达到富营养化标准。
定点大、小潮DIN/DIP为18.01~21.47,平均值为19.85(见图4A),走航站DIN/DIP为18.55~33.41,平均值为26.02(见图4B),均介于8~30,故三沙湾水体总体上不存在氮、磷营养盐限制。仅有个别水域存在磷限制(30站位和26站位,DIN/DIP大于30)(见图4B)。
上述结果表明,三沙湾水质已处于严重污染和富营养化水平。另外,定点站P1和12个走航站DIN/DIP范围基本小于但接近30(磷限制比例阈值),甚至个别水域大于30(30站位和26站位)的结果(见图4),表明三沙湾存在磷限制的风险。
2.3 陆源污染对三沙湾营养盐含量的影响
定点站P1位于宁德大金溪河口,其水质浓度变化主要受城区排放水的浓度影响。P1站SiO3-Si、NO3-N、NH4-N、PO4-P和SSC的浓度(盐度最小时段),分别是海水的2.5倍、1.2倍、3.6倍、2倍和6倍(盐度最大时段),且NH4-N的浓度总体上显著大于NO3-N浓度(见图2),说明大金溪河口水体中营养盐主要来源于宁德城区排放水,且污水处理水平较低,氨氮尚未完全硝化为硝酸盐[27],其机制在于排污口附近过高的氨浓度抑制了氨氧化菌(AOB)的活性,导致氨氧化速率下降,进而引起氨氮持续保持高浓度[28]。三沙湾3个断面从陆向海NO3-N和SiO3-Si的浓度不断下降(见图3B、图3C),11站(毗邻P1站)的NH4-N、PO4-P浓度异常高于其他站的结果(见图3E、图3F),表明三沙湾的NO3-N、SiO3-Si、NH4-N、PO4-P等营养盐主要来源于陆源排放,另外城区污水处理水平低,氨氮硝化作用不完全,进一步导致营养盐含量增高。而且,随着三沙湾区域陆域污染物排放通量不断增加,工业固体废弃物和废水排放量分别由2014年的289.98万吨和10476.8万吨增加到2017年的490.9万吨和11824.8万吨,农田化肥和城镇生活污水的氨氮年平均排放量达276.17吨[29],这种状况导致其水质向更差的方向发展。
2.4 盐度与三沙湾营养盐含量的关系
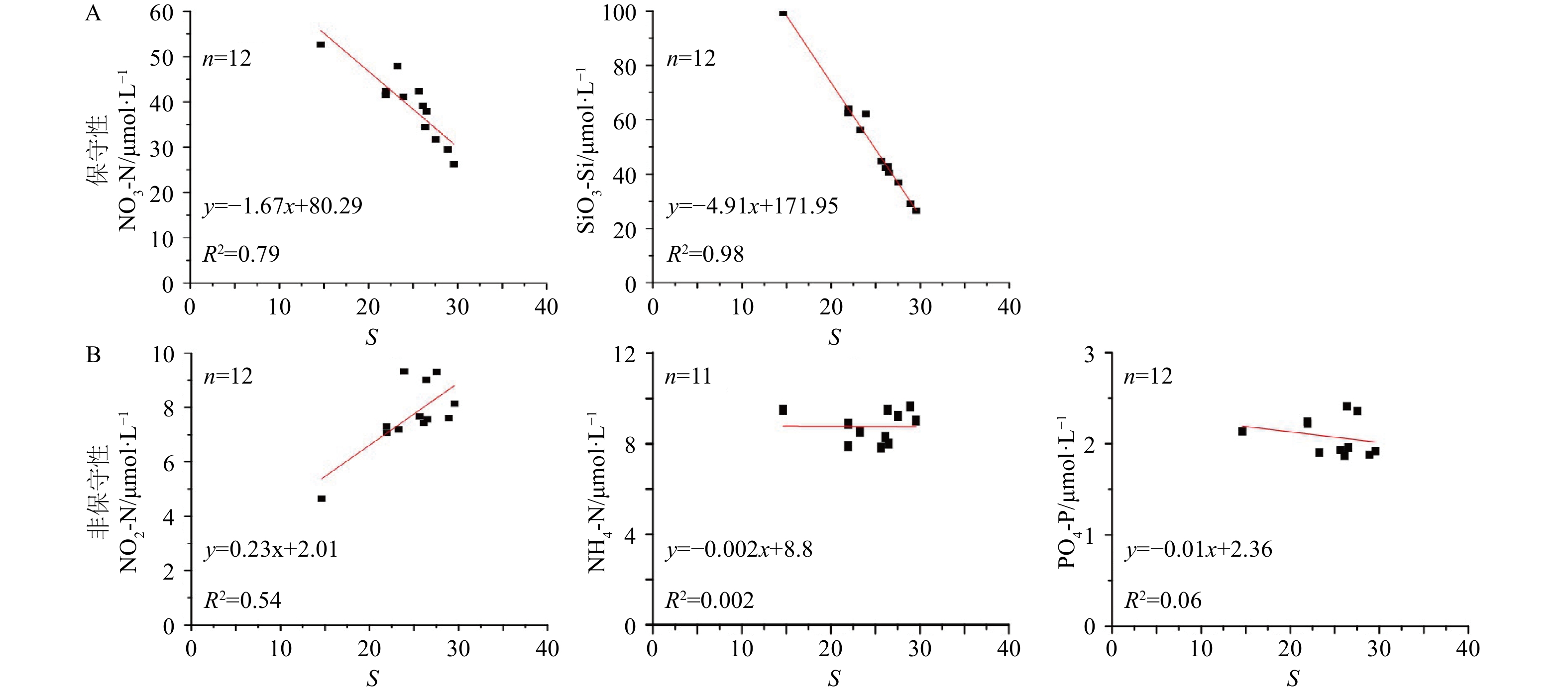
三沙湾3个断面从陆向海的NO3-N和SiO3-Si浓度随盐度增加不断减小(见图3A、图3B、图3C),其与盐度的相关性分析R2分别达到0.79和0.98(见图5A),说明三沙湾内NO3-N和SiO3-Si变化的主要机制是海水的稀释扩散作用,受生物过程的影响较小。另外,3个断面夏季的NO3-N和SiO3-Si随盐度变化的平均梯度[(μmol/L)/‰]分别约为1.6和4.9,呈现较大的差异(见图3B、图3C、图5A),这种受海水稀释作用与化学反应移除的过程称为保守性行为[30-33]。其次,长江口、闽江口夏季的NO3-N和SiO3-Si随盐度变化的梯度[(μmol/L)/‰]分别为1.8、2.8、3.3和2.8[34-35]。与上述河口相比,三沙湾的保守性体现在NO3-N梯度小,而SiO3-Si梯度大,这种独特性可能与海水的物理混合稀释及生化作用的强度不同有关,其机理值得进一步研究。
2.5 湾内养殖对三沙湾营养盐含量的影响
在很多河口海岸区域,NO2-N、NH4-N和PO4-P与盐度的关系表现为:相关性很差,总体上呈负相关(随盐度增加而减少),并且回归方程的斜率很小(随盐度变化的梯度很小)[34-36]。这种变化的机制主要是水域内复杂的生物地球化学过程中产生了内源性NO2-N、NH4-N和PO4-P营养盐,抵消了海水对外源营养盐的稀释作用和离子化学移除作用,这种营养盐与盐度的非线性关系,被称为非保守性行为[32, 37]。
但是,三沙湾NO2-N、NH4-N和PO4-P与盐度的关系却呈现出独特性,尽管NO2-N、NH4-N和PO4-P与盐度的相关性分析R2只有0.54、0.03和0.015(见图5B),并且NH4-N和PO4-P随盐度增加出现微减趋势,但NO2-N却随盐度增加而增加(见图3D、图3E、图3F)。我们认为,这种独特结果尤其是NO2-N随盐度增加而增加的异常特征是三沙湾大规模的湾内养殖以及过度投放饵料所致。湾内养殖中鱼类等的排泄物和投放饵料导致湾内浮游植物生物量以及微生物量远高于其他区域,浮游植物和微生物的生长吸收消耗大量的NH4-N和PO4-P,同时排泄和分解也会产生NO2-N、NH4-N和PO4-P[38-39];随着气候的变化,特别是养殖水体中,较高的温度能够促进硝化作用,使NH4-N进一步转化为NO2-N和NO3-N[40-41],水体中氨氧化速率大于亚硝酸盐的氧化速率,这可能也是亚硝酸盐积累的原因[27];另外,高盐度能够促进悬浮颗粒和沉积物释放出NH4-N和PO4-P[35],两种作用使得NH4-N和PO4-P随盐度增加变化不明显(见图5B),由于NO2-N是毒性物质,微生物和浮游植物的生长消耗不能降低其浓度,但微生物和浮游植物排泄和死亡分解却能大大增加其浓度[42],这种机制导致NO2-N随盐度增加而增加的异常特征(见图5B)。
据统计,每生产1 吨鱼通过饵料带进养殖水环境的氮达78 kg,通过鱼类的粪便和尿液约有40 kg溶解氮进入水体[43-44];1000 m2网箱(平均鱼产量1.7~2.3 t)投放饵料中的总磷有77%~88%进入养殖环境中[45]。另外,三沙湾的养殖已成主导产业,2017年海水养殖面积约408.74 km2,淡水养殖面积103.38 km2[29],巨量饵料的投放以及湾内与外海缓慢的水交换能力,增加了水体中NH4-N、PO4-P和NO2-N的浓度,导致其独特的非保守性行为。
综上所述,三沙湾营养盐一方面来源于陆地上大量的工农业废水和生活污水,另一方面来源于湾内养殖所带来的残饵和鱼类排泄物等。而且三沙湾是个口小腹大的海湾,湾内外海水交换较慢,因此该区氮、磷营养盐含量较高,导致海湾富营养化程度日趋严重。因此,控制沿岸工农业废水、生活污水的排放,实行科学合理的网箱养殖,对于三沙湾海域的可持续发展具有重要意义。
3 结 论
(1) 陆源污染尤其是近岸城区的排放严重影响和改变了湾内水质。三沙湾大金溪落潮盐度最小时期(宁德城区排放水)水质污染物浓度显著高于涨潮盐度最大时期(海水)的水质浓度,NO3-N、NH4-N、SSC、SiO3-Si和PO4-P等在盐度最小时期的浓度值分别是盐度最大时期的1.2、3.6、6、2.5和2倍。从陆向海受陆源城区污染的影响,营养盐的浓度总体上不断降低。
(2) 湾内养殖深刻影响和改变了NO2-N、NH4-N、PO4-P随盐度变化的非保守性行为,可能是导致湾内NH4-N、PO4-P和NO2-N浓度持续保持较高水平的原因。
(3) 陆源污染和湾内养殖导致三沙湾水质已处于严重污染和富营养化水平,加剧了富营养化引发的赤潮等生态灾害的风险。
-
表 1 水域营养级综合评价标准
Tab. 1 Classification of nutrient levels
等级 富养级 DIN/μmol·L−1 PO4-P/μmol·L−1 N:P I 贫营养 <14.28 <0.97 8~30 II 中度营养 14.28~21.41 0.97~1.45 8~30 III 富营养 >21.41 >1.45 8~30 IVP 磷限制中度营养 14.28~21.41 >30 VP 磷中等限制潜在性富营养 >21.41 30~60 VIP 磷限制潜在性富营养 >21.41 >60 IVN 氮限制中度营养 0.97~1.45 <8 VN 氮中等限制潜在性富营养 >1.45 4~8 VIN 氮限制潜在性富营养 >1.45 <4 -
[1] 郑钦华. 福建三都澳渔业水域水环境监测与评价[J]. 宁德师专学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 22(3): 250-254, 267. [2] 郑钦华. 三沙湾重点水产养殖水域理化变化特征及富营养化状况[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2017, 36(1): 24-30. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2017.01.004 [3] 邵 留, 于克锋, 吴海龙, 等. 三沙湾海域水质周年变化分析与评价[J]. 上海海洋大学学报, 2014, 23(2): 228-237. [4] 沈林南, 李 超, 吴祥恩, 等. 夏冬季三沙湾海水营养盐含量的时空变化特征及与环境因子的相关性[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2014, 33(4): 553-561. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.2095-4972.2014.04.014 [5] 房月英. 三都湾赤潮监控区海水富营养化与赤潮发生的关系研究[D]. 福州: 福建师范大学, 2008. [6] 蔡清海. 福建三沙湾海洋生态环境研究[J]. 中国环境监测, 2007, 23(6): 101-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6002.2007.06.028 [7] 蔡小霞, 潘建明, 于培松, 等. 浙江近岸典型港湾的营养盐行为特征[J]. 海洋通报, 2013, 32(5): 488-493. doi: 10.11840/j.issn.1001-6392.2013.05.002 [8] LI S Y, BUSH R T. Rising flux of nutrients(C, N, P and Si) in the lower Mekong River[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2015, 530: 447-461. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.10.005
[9] GRIZZETTI B, BOURAOUI F, ALOE A. Changes of nitrogen and phosphorus loads to European seas[J]. Global Change Biology, 2012, 18(2): 769-782. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2011.02576.x
[10] WANG X L, CUI Z G, GUO Q, et al. Distribution of nutrients and eutrophication assessment in the Bohai Sea of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2009, 27: 177-183. doi: 10.1007/s00343-009-0177-x
[11] 黄 标, 钱鲁闽, 刘家富. 福建三都澳水产养殖区水体氮磷含量及潜在性富营养化程度分析[J]. 台湾海峡, 2002, 21(4): 411-415. [12] 赵卫红. 福建近岸海域水质现状及污染防治对策[J]. 福建地理, 2006, 21(2): 107-109, 115. [13] LU X T, LU Y L, CHEN D L, et al. Climate change induced eutrophication of cold-water lake in an ecologically fragile nature reserve[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 75: 359-369. doi: 10.1016/j.jes.2018.05.018
[14] WOJCIECH M, SOYDOA V, THONGSAMER T, et al. The food-water quality nexus in periurban aquacultures downstream of Bangkok, Thailand[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 695: 133923. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133923
[15] DU R B, LIU L M, WANG A M, et al. Effects of temperature, algae biomass and ambient nutrient on the absorption of dissolved nitrogen and phosphate by Rhodophyte Gracilaria asiatica[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2013, 31(2): 353-365. doi: 10.1007/s00343-013-2114-2
[16] 彭云辉, 王肇鼎. 珠江河口富营养化水平评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1991, 10(3): 7-13. [17] 侯昱廷, 高爱国, 林建杰, 等. 闽江河口营养盐的季节变化及混合行为[J]. 厦门大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 55(4): 540-546. [18] 沈德福, 张光英. 闽东滩涂养殖对三都澳环境与资源的影响浅析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2015, 43(6): 247-249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2015.06.092 [19] 马祖友, 夏永健, 石志洲, 等. 2011年三沙湾增养殖区水环境质量评价[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2013, 30(7): 75-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2013.07.018 [20] 陈聚法, 赵 俊, 孙 耀, 等. 桑沟湾贝类养殖水域沉积物再悬浮的动力机制及其对水体中营养盐的影响[J]. 海洋水产研究, 2007, 28(3): 105-111. [21] GB 17378–2007, 海洋监测规范[S]. [22] GB 3097–1997, 海水水质标准[S]. [23] 林晓娟, 高 姗, 仉天宇, 等. 海水富营养化评价方法的研究进展与应用现状[J]. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(4): 373-384. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.04.0373 [24] 杨美兰, 钟 彦, 林燕棠. 大鹏湾南澳养殖水域的氮、磷含量特征[J]. 热带海洋, 1998, 17(2): 74-80. [25] LIANG S X, WU H, LI H B, et al. Assessment of the spatial and temporal water eutrophication for Lake Baiyangdian Based on integrated fuzzy method[J]. Journal of Environmental Protection, 2013, 4(1): 120-125. doi: 10.4236/jep.2013.41013
[26] 郭卫东, 章小明, 杨逸萍, 等. 中国近岸海域潜在性富营养化程度的评价[J]. 台湾海峡, 1998, 17(1): 64-70. [27] 俞 盈, 付广义, 陈繁忠, 等. 水体中三氮转化规律及影响因素研究[J]. 地球化学, 2008, 37(6): 565-571. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2008.06.006 [28] 何碧烟, 欧光南, 吕禹泽, 等. 杏林湾水体的硝化作用及其影响因素研究[J]. 微生物前沿, 2016, 5(4): 71-80. [29] 宁德市统计局, 宁德统计年鉴2018年[EB/OL]. (2018-10-31). http://tjj.ningde.gov.cn/xxgk/ndsj/201901/t20190104_883507.htm. [30] CHEN S T. Biogeochemical behavior of nutrients and their fluxes in the Minjiang River estuary[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 1997, 15(2): 150-155. doi: 10.1007/BF02850685
[31] WANG B D, TU J B. Biogeochemistry of nutrient elements in the Changjiang (Yangtze River) Estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2005, 7(2): 72-79.
[32] 于立霞, 简慧敏, 王兆锟, 等. 夏季辽河口各形态营养盐的河口混合行为[J]. 海洋科学, 2011, 35(12): 68-74. [33] 杨 斌, 方怀义, 钟秋平, 等. 钦州湾夏季营养盐的分布特征及富营养化评价[J]. 海洋通报, 2012, 31(6): 640-645. [34] 王正方, 姚龙奎, 阮小正. 长江口营养盐(N、P、Si)分布与变化特征[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 1983, 14(4): 324-332. [35] 叶 翔, 陈 坚, 暨卫东, 等. 闽江口营养盐生物地球化学过程研究[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(2): 375-383. [36] 张远辉, 王伟强, 黄自强, 等. 九龙江口盐度锋面及其营养盐的化学行为[J]. 海洋环境科学, 1999, 18(4): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.1999.04.001 [37] 张 经. 近海生物地球化学的基本原理[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2009. [38] 韦蔓新, 赖廷和, 何本茂. 广西钦州内湾贝类养殖海区三氮的含量和百分组成[J]. 台湾海峡, 2001, 20(4): 441-446. [39] 王文涛, 曹西华, 袁涌铨, 等. 2012年长江口及其邻近海域营养盐分布的季节变化及影响因素[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2016, 47(4): 804-812. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20160100017 [40] DAI M H, WANG L F, GUO X H, et al. Nitrification and inorganic nitrogen distribution in a large perturbed river/estuarine system: the Pearl River Estuary, China[J]. Biogeosciences, 2008, 5(5): 1227-1244. doi: 10.5194/bg-5-1227-2008
[41] TESTA J M, MURPHY R R, BRADY D C, et al. Nutrient-and climate-induced shifts in the phenology of linked biogeochemical cycles in a temperate estuary[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2018, 5: 114. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2018.00114
[42] 林培华, 黄伟卿. 三都澳水产养殖区表层水营养盐周年变化及发展趋势[J]. 宁德师范学院学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 25(2): 141-145. [43] FOLKE C, KAUTSKY N, TROELL M. The costs of eutrophication from salmon farming: implications for policy[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 1994, 40(2): 173-182. doi: 10.1006/jema.1994.1013
[44] HALL P O J, HOLBY O, KOLLBERG S, et al. Chemical fluxes and mass balances in a marine fish cage farm. IV. Nitrogen[J]. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 1992, 89: 81-91. doi: 10.3354/meps089081
[45] PHILLIPS M J, BEVERIDGE M C M, ROSS L G. The environmental impact of salmonid cage culture on inland fisheries: present status and future trends[J]. Journal of Fish Biology, 1985, 27(sA): 123-137. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8649.1985.tb03236.x
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 郭昊辰. 基于水质单因子指数的水体污染源识别与指标阶段变化监测研究. 环境科学与管理. 2024(09): 129-133 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曹诺彤,李青生,蒋金龙. 三沙湾氮磷时空变化及其影响因素分析. 海洋开发与管理. 2024(09): 79-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 姚开雪,印瑞,王洋,陈峰,李振华. 乐清湾海域营养盐时空分布特征及其富营养化评价. 海洋开发与管理. 2024(09): 121-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 雷灵逸,王飞鹏,臧昆鹏,吕小龙,张智,杨丽阳,穆景利. 中国东南沿海典型养殖海湾:三沙湾海——气界面甲烷扩散通量及影响因素研究. 地球科学进展. 2024(11): 1156-1168 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张永年. 基于哨兵二号数据的三沙湾叶绿素a浓度时空变化分析. 现代测绘. 2024(06): 50-55+84 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 黄亚玲,李悦,陈志平,李荣茂,陈火荣,穆景利. 三沙湾营养盐时空分布特征及其潜在影响因素识别. 海洋环境科学. 2023(03): 440-448 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. Junwei Zhu,Yifan Ma,Lingfeng Huang,Wenjing Zhang. Homogeneous selection is not always important in bacterial community in the eutrophic enclosed bay. Ecological Processes. 2022(02): 77-87 .  必应学术
必应学术
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: