Research on the origin traceability of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) in Liaoning and Shandong based on the compound-specific carbon isotope analysis of amino acids
-
摘要:
本研究利用气相色谱-燃烧-同位素比值质谱仪(GC-C-IRMS)测定黄渤海区域不同地区(辽宁、山东)刺参氨基酸的相对含量及其碳稳定同位素组成特征,探讨以这些指标作为海参产地溯源的可行性。测定结果显示,脯氨酸(F=4.13)、亮氨酸(F=9.08)、酪氨酸(F=8.78)的相对含量在两地之间存在显著差异,通过主成分分析法对氨基酸相对含量做降维处理后未能将两地海参做出明显区分;辽宁刺参氨基酸的δ13C值范围是-24.54‰~-11.87‰,山东刺参氨基酸的δ13C值范围是-27.36‰~-16.42‰,二者之间多数氨基酸的δ13C值呈现显著差异,选取其中的两种氨基酸Tyr和Ser的δ13C值作为指标,可明显区分二者。结果表明氨基酸的碳稳定同位素组成相比于其相对含量是作为区分辽宁、山东刺参更准确的指标。相关结论能为氨基酸的稳定同位素分析技术应用于刺参产地溯源研究提供理论依据。
Abstract:In this study, we measured the relative contents and stable carbon isotope compositions of amino acids(AAs) in Apostichopus japonicus from Liaoning and Shandong by GC-C-IRMS, and evaluated its applicability in establishing the origin traceability of Apostichopus japonicus.Results showed that, the relative content of Pro(F=4.13), Ile(F=9.08) and Tyr(F=8.78) revealed significant difference between those two locations, and AAs compositions combined with principal component analysis did not discriminate samples of those two locations; the δ13C values of A. japonicus from Liaoning ranged from -24.54‰~-11.87‰ and the δ13C values of A. japonicus from Shandong ranged from -27.36‰~-16.42‰, most of the AAs δ13C values revealed significant difference between those two locations, we selected two AAs:Tyr and Ser, and their δ13C values could clearly discriminate samples of those two locations.So the stable carbon isotope composition of AAs is more precise than the AAs compositions for discriminating the samples of A. japonicus between Liaoning and Shandong.Thus, compound-specific carbon isotope analysis of AAs will provide a theoretical basis for establishing the traceability of the geographical origins of A.japonicus.
-
Keywords:
- Apostichopus japonicus /
- stable isotopes /
- amino acids /
- geographic traceability
-
海参隶属于棘皮动物们,海参纲。其作为一种海珍品,具有很高的营养价值,并已被证实具有抗凝血、抗肿瘤等多种生物活性[1],在功能性食品开发方面有非常良好的前景。由于其良好的经济价值,刺参养殖也逐渐成为黄渤海海域渔业的支柱产业。近年来仅辽宁和山东地区的刺参产值就已超过400亿人民币[2],得益于其独特产地优势的优良品质,但这些刺参的固有原产地优势越来越受到伪劣假冒产品的严重挤压,由于缺乏监督和管理,市场上出现大量以次充好的海参产品,造成不良的经济和社会影响,食品安全问题变得日益突出。因此评价刺参来源的真实性显得尤为重要。
氨基酸是生物代谢过程中起重要作用的物质,生物体氨基酸含量与品种、年龄、养殖环境等因素有关,而相对于品种和年龄,氨基酸含量受到环境影响很显著[3]。因此其组成含量作为一个有效的工具现在已经被广泛应用于地理溯源,已有研究区分了不同地域的酒类、蜂蜜、果汁、禽类等[4-7],但对于海洋动物的溯源未见报道,原因可能是由于海洋动物的活动范围比较广泛,摄食类型比较复杂,应用此种技术手段并不能得到令人满意的效果。
目前稳定同位素溯源技术已在水产品的产地溯源研究中得到了广泛的应用,被认为是最有效的产地溯源技术,大多数研究都是通过分析样品全样的碳稳定同位素作为指标[8-9],但有研究表明,无机碳源在被消费者摄食过程中,不同营养成分的碳骨架(蛋白质、水、糖类)会转化成消费者不同的组织,产生了不同的δ13C值[10],所以只以全样的碳稳定同位素作为产地溯源的指标并不能完全令人信服。
现阶段随着IRMS技术的发展,已有方法能够分析特征化合物的稳定同位素。因此可以结合上述两种技术,对生物个体的氨基酸稳定同位素进行分析,得到其更详细的信息。本研究测定了来自辽宁和山东不同地区刺参体壁氨基酸含量以及其碳稳定同位素组成特征,评价了上述两种技术作为刺参地理溯源的可行性,旨在找到一个更准确的区分不同地理来源的刺参的指标,为刺参的产地溯源提供理论基础,从而建立一个能够准确追溯刺参产地来源的方法。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试剂
18种氨基酸(丙氨酸、氯化铵、精氨酸、天冬氨酸、半胱氨酸、谷氨酸、甘氨酸、组氨酸、异亮氨酸、亮氨酸、赖氨酸、蛋氨酸、苯丙氨酸、脯氨酸、丝氨酸、苏氨酸、酪氨酸、缬氨酸)混标≥98%(西格玛)、阳离子交换树脂(安捷伦)、盐酸、甲醇、二氯甲烷、乙酸乙酯、异丙醇、吡啶、氯化亚砜、特戊酰氯(天地)
1.2 样品的采集和处理
刺参样品于2015年11月采自山东和辽宁不同海域,采样的环境条件以及样品的详细信息见表 1。
表 1 采样地点的环境条件以及样品信息Tab. 1 The environmental conditions of the sampling locations and the sample informations
采集的刺参样品样品都是3 a龄成参,在运输过程中都以无菌塑料袋包装后冷藏保存。带回实验室后,立即将样品解剖,用超纯水洗掉杂质,取其体壁在-80℃下冷冻保存。实验前再将需要的完全冷冻的样品取出,在-50℃下冻干48 h然后用研钵和研杵将冻干样品研磨成粉末并过80 μm的筛子,得到样品的粉末。
1.3 氨基酸的提取和纯化
准确称取20 mg的海参粉末样品于16 mm×100 mm pyrex试管中,加入2 mL 6 M的HCl。向试管中冲N2 1 min,完全置换出其中的空气。将密封的试管放置于恒温干燥箱内,110℃水解24 h。水解后得到的水解液在430 g下离心10 min,上清液保留,用强阳离子交换柱来纯化氨基酸。
1.4 氨基酸衍生化
由于氨基酸是两性离子,不易挥发,运用GC-IRMS法分析氨基酸必须将其转化成易挥发的离子,这就需要将氨基酸衍生化,本实验采用的方法可最终将氨基酸衍生化成相对应的N-新戊酰基,O-异丙醇酯(NPP)[11],具体如下:向氨基酸标准品或提取出来的的样品加入2 mL溶于异丙醇的1 M的氯化亚砜100℃酯化1 h,然后60℃N2吹干,干燥物用吡啶溶解,再加入新戊酰氯60℃酰化30 min,生成NPP,反应完全后待液体冷却,向其中加入2 mL二氯甲烷,加入到6 cm硅胶层析柱(内径4 mm,200~400目)除去杂质和多余的酰化剂,收集到的液体在室温下用温和的N2吹干即为纯化的衍生物NPP氨基酸酯,最后将其溶于0.2 mL乙酸乙酯待测。
1.5 GC-C-IRMS分析
色谱质谱条件如下:色谱柱为DB-5MS毛细管色谱柱(60 m × 0.25 mm ID,0.25 μm Film)升温程序为:起始温度70℃,保留1 min,3℃/min升到220℃,然后再10℃/min升到300℃,保留8 min。载气为高纯氦气(纯度为99.999%),载气流速为1.2 mL/min,进样口温度为280℃,进样模式为不分流。
Ei离子源:电子能量,70 eV;温度250℃;接口温度250℃,选取SCAN模式,质量扫描范围为m/z 50~490,溶剂延迟4 min。
1.6 数据修正和分析
通过对标准品的测定可得到16种氨基酸的保留时间,以这些保留时间作为标准可判断样品各个氨基酸衍生物出峰的具体时间。根据其峰面积占总数的比例,可以得到各个氨基酸的相对含量。
稳定同位素值(δ)的计算方式如下:

式中:R样品是样品的13C/12C的值;R标准是国际同位素标准(VPDB)的13C/12C的值,即CO2的标准气体采用国际通用的PDB标准气体。本实验室样品的δ13C的测量精度用实验室内标光谱重复测定确定为±0.09‰。
在对氨基酸氨基酸衍生品δ13C值的测定,由于衍生品引入额外的碳原子,想得到氨基酸真正的δ13C值,需要对其结果通过如下公式进行矫正[12]:

式中:Ndaa是衍生化后样品的总碳数;δdaa是衍生化后样品的δ13C值;δe是经验校正因子;Nd是衍生试剂的碳数;δd是衍生试剂的δ13C值;Naa是对应的天然氨基酸的碳数。
1.7 统计学分析
所有数据都是通过软件SPSS 19进行分析的。其中本文的所有数值都是以平均值±标准差的形式给出。两个地点氨基酸之间相对含量和δ13C的差异应用了独立样本T检验法,对于各个不同地点每个氨基酸相对含量数据的分析我们应用了主成分分(PCA)析法对其进行群组聚类。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 辽宁、山东刺参的氨基酸相对含量
动物体的氨基酸分为必需氨基酸和非必需氨基酸,其中必需氨基酸是动物只能从食物中获取的氨基酸,无法通过自身合成;非必需氨基酸是动物体可以自身合成的氨基酸[13]。辽宁、山东采集的刺参氨基酸相对含量如表 2所示。
表 2 辽宁山东刺参氨基酸相对含量/(%)Tab. 2 The relative content of amino acids for A.japonicus caught in Liaoning and Shandong/ (%)
总体上看,两地刺参氨基酸相对含量特征相似,多数氨基酸都未表现出差异性,尤其是必需氨基酸,只有Leu存在显著差异,McMahon等发现鱼类与其饵料氨基酸组成特征有一定相关性[14],并且必需氨基酸的相关性更强,因此可以推断,由于山东、辽宁两地地理位置离得较近,并且两地的采样点都分布于黄渤海湾,环境条件相似导致其优势种相似,所以两地刺参食源种类相似,造成二者多数氨基酸尤其是必需氨基酸组成特征相似;非必需氨基酸中Pro和Tyr存在显著差异,其中造成Pro含量差异的原因,已有大量研究表明细菌和植物在高盐度、温度、重金属等环境胁迫下,会导致其Pro含量显著增加[15-17],由表 1可知山东地区的海水温度和盐度都比辽宁地区略高,所以可能会造成山东地区刺参食源的Pro相对含量较高,导致了该地区刺参Pro的含量较高,进而造成了这种差异性。此外,研究发现Ala在这两个地区的样品中标准偏差很大,可能是由于这些样品虽然来自同一省份,但分别来自不同的海域的不同地区,Ala属于非必需氨基酸,可以通过动物体自身合成,要在谷-丙转氨酶作用下通过丙酮酸合成丙氨酸,这种酶的活性会受到温度和盐度等环境条件的影响[14],因此这些不同地点的刺参在合成Ala时可能会表现出不同的特征,从而导致这种现象。
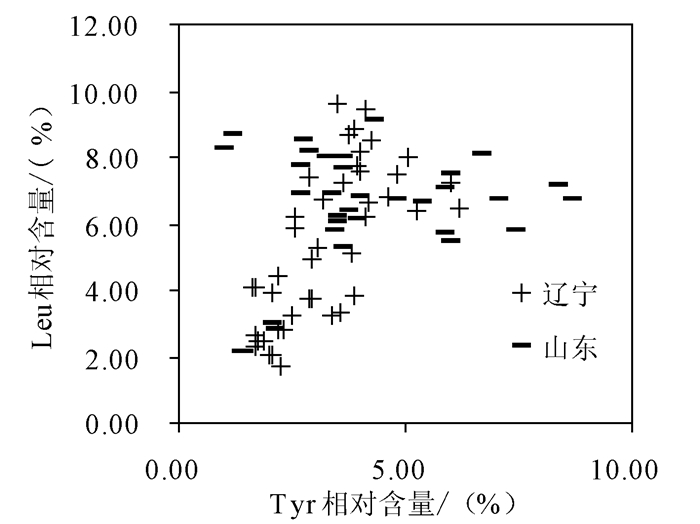
根据得到的数据,分别在必需氨基酸和非必需氨基酸中选取差异性最大的两种氨基酸,Tyr(F=8.78)和Leu(F=9.08)绘制成散点图,如图 1所示。发现仅以这两种氨基酸并不能完全区分辽宁和山东的刺参,大部分都重叠在一起。为了得到更明确的区分,我们将得到的10种氨基酸进行主成分分析,结果如表 3所示,可知此两个主成分的贡献率分别为47.26%、17.67%,其中第一个主成分主要综合了样品中Ala、Pro、Glu、Tyr、Leu、Ile、Phe的含量信息,第二个主成分主要综合了样品中Gly、Ser、Val的含量信息。
表 3 各主成分变量特征向量及方差贡献率Tab. 3 The eigenvectors and variance contribution of variance of the principal components
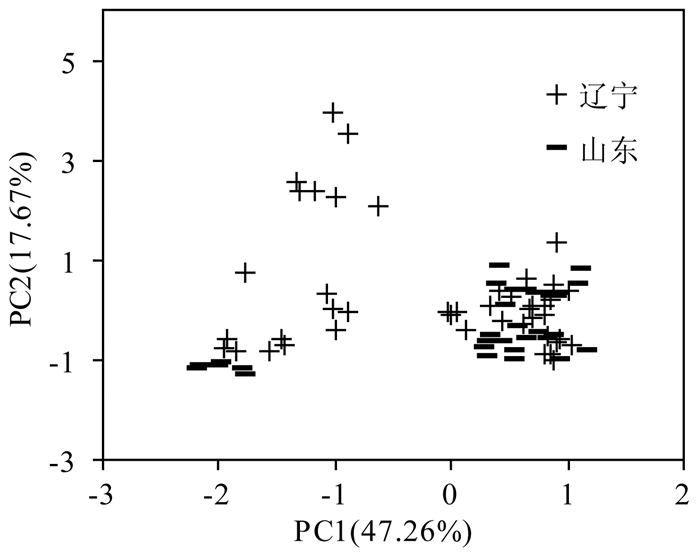
利用这两个主成分的标准化得分绘制的散点图见图 2,结果表明只有部分样品被区分开,仍有一些样品的数据重叠在一起,此结果说明仅以氨基酸相对含量与多元分析作为指标对辽宁、山东刺参的区分并不理想,有一定的局限性,为得到更准确的结果,需要更准确的方法。
2.2 辽宁、山东刺参的氨基酸δ13C值
利用NPP衍生化方法,测定了黄渤海刺参中能有效分离的氨基酸的δ13C值,结果如表 4,从总体看,辽宁、山东刺参多数氨基酸的δ13C值差异显著,范围分别为-24.54‰~-11.87‰、-27.36‰~-16.42‰,辽宁刺参氨基酸的δ13C值整体比山东刺参的稍高。其中非必需氨基酸中除了Glu都表现出显著差异,必需氨基酸中除Val和Phe也都表现出显著差异。造成这种差异的原因,是由于不同区域的初级生产者氨基酸合成和代谢过程会产生高度的多样性,因此他们的氨基酸会产生独特的δ13C标签,已有研究表明,消费者在摄食后,不同营养级之间的必需氨基酸几乎没有发生同位素分馏现象,而非必需氨基酸会出现不同程度的同位素分馏。也就是说不同营养级的消费者在摄食过程中,其必需氨基酸的δ13C值几乎保持不变,因此由于不同地区初级生产者都有自己独特的氨基酸δ13C标签,所以造成了消费者必需氨基酸δ13C的差异;而非必需氨基酸不仅可以从食物中获取并且能够自身合成,在合成不同氨基酸的过程中,对不同碳源的利用率也有所不同,这样的特性造成了消费者非必需氨基酸的δ13C标签相比于必需氨基酸有更高的多样性[14]。在本研究中,也恰好表现出与此相似的情况,两不同省份的刺参非必需氨基酸的δ13C值相比于必需氨基酸差异性更显著,其中Gly、Pro、Ser、Tyr此4种氨基酸P值<0.001,而必需氨基酸中只有Ile一种氨基酸P值<0.001,在这些氨基酸中Ile是唯一的必需氨基酸,其δ13C值就完全继承了所在区域初级生产的δ13C值,由此可知即使两地环境条件相似,也会存在这种具有不同的δ13C标签的氨基酸。其中Phe的δ13C值在二者之间的差异性最不显著(F=1.24),已有很多研究发现,由于Phe是芳香族氨基酸,合成过程比较稳定,所以其δ13C受环境条件影响不大,在食物网结构研究中常被应用为标志性氨基酸[14, 18],本实验结果与这一结论吻合;Tyr的δ13C值在二者之间的差异性最显著(F=59.63),由于动物体很大一部分Tyr需要以Phe作为前体在苯丙氨酸羟化酶的催化作用下合成,也被称为半必需氨基酸,而本研究中Phe的δ13C值在两地之间差异并不明显,因此Tyr的δ13C值更能反应出两地刺参内源性代谢合成的特征,所以推断由于氨基酸生物合成过程受不同环境影响(生物酶活性、合成速率等)产生了不同程度的同位素分馏现象,进而造成了两地刺参Tyr δ13C值的差异性。
表 4 辽宁山东刺参氨基酸δ13C值Tab. 4 The δ13C values of amino acids for A.japonicus caught in Liaoning and Shangdong
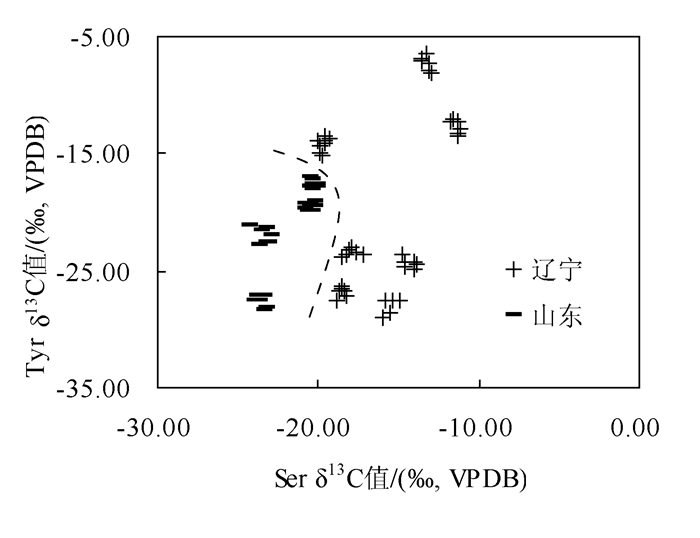
根据得到的数据,选取两种氨基酸,Tyr(F=59.63)、Ser(F=23.62)绘制散点图,如图 3所示,发现此两种氨基酸的δ13C值可将两地刺参很明显的区分开,几乎没有重叠部分,分别位于虚线的左右两侧。可见氨基酸δ13C值相比于其相对含量是区分辽宁、山东刺参更显著的指标,无需借助多元统计学分析,即可明显区分二者。
3 结论
(1) 本研究测定并分析了辽宁、山东刺参氨基酸相对含量及其δ13C值,结果显示,首先对于氨基酸的相对含量,发现其在两地刺参之间的差异性不显著,以其中差异性相对显著的两种氨基酸作为指标,未能明显区分二者,我们采用主成分分析法对测得的全部氨基酸相对含量数据进行分析,也并未得到理想的区分效果。然后我们分析了两地刺参的δ13C值,发现多数氨基酸的δ13C值差异显著,其中非必需氨基酸的显著性要高于必需氨基酸,在非必需氨基酸中选取两种氨基酸Tyr和Ser的δ13C值作为指标,即可将二者明显区分。可得出结论,氨基酸的碳稳定同位素组成相比于其相对含量是作为区分辽宁、山东刺参产地来源更准确的指标,因此这种方法是海参产地溯源更有前景的方法。
(2) 本研究中仅采集了黄渤地区的部分代表产地的刺参,今后可以通过扩大采样量和采样地点进一步证实此方法的准确性。此外,还可以通过采集不同地点刺参食物来源,探究造成这些海参氨基酸稳定同位素区别的环境因素。
-
表 1 采样地点的环境条件以及样品信息
Tab. 1 The environmental conditions of the sampling locations and the sample informations

表 2 辽宁山东刺参氨基酸相对含量/(%)
Tab. 2 The relative content of amino acids for A.japonicus caught in Liaoning and Shandong/ (%)

表 3 各主成分变量特征向量及方差贡献率
Tab. 3 The eigenvectors and variance contribution of variance of the principal components

表 4 辽宁山东刺参氨基酸δ13C值
Tab. 4 The δ13C values of amino acids for A.japonicus caught in Liaoning and Shangdong

-
[1] 闫冰, 李玲, 易杨华.海参多糖的生物活性研究概况[J].药学实践杂志, 2004, 22(2):101-103. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXSJ200402013.htm [2] ZHANG X F, LIU Y, LI Y, et al.Identification of the geographical origins of sea cucumber (Apostichopus japonicus) in northern China by using stable isotope ratios and fatty acid profiles[J].Food Chemistry, 2017, 218:269-276. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.08.083
[3] 刘兴勇, 林涛, 刘宏程, 等.基于水解氨基酸分析山羊肉的产地溯源[J].现代食品科技, 2013(11):2788-2792. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZSP201311042.htm [4] 崔珊珊, 胡卓炎, 余恺, 等.不同产地妃子笑荔枝果汁的氨基酸组分[J].食品科学, 2011, 32(12):269-273. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=spkx201112059 [5] DAVIES A M C.The application of amino acid analysis to the determination of the geographical origin of honey[J].International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 1976, 11(5):515-523. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1694b22123a339b463e8cc7e55d4c22f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[6] XU W P, SONG Q S, LI D X, et al.Discrimination of the production season of Chinese green tea by chemical analysis in combination with supervised pattern recognition[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2012, 60(28):7064-7070. doi: 10.1021/jf301340z
[7] 张颖, 张健, 史珅.氨基酸含量分析判别梅鹿辄葡萄原酒产地[J].食品研究与开发, 2011, 32(5):9-12. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=spyk201105006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [8] ORTEA I, GALLARDO J M.Investigation of production method, geographical origin and species authentication in commercially relevant shrimps using stable isotope ratio and/or multi-element analyses combined with chemometrics:an exploratory analysis[J].Food Chemistry, 2015, 170:145-153. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.08.049
[9] RACO B, DOTSIKA E, POUTOUKIS D, et al.O-H-C isotope ratio determination in wine in order to be used as a fingerprint of its regional origin[J].Food Chemistry, 2015, 168:588-594. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.07.043
[10] SCHWARCZ H P.Some theoretical aspects of isotope paleodiet studies[J].Journal of Archaeological Science, 1991, 18(3):261-275. doi: 10.1016/0305-4403(91)90065-W
[11] METGES C C, PETZKE K J, HENNIG U.Gas chromatography/combustion/isotope ratio mass spectrometric comparison of N-acetyl-and N-pivaloyl amino acid esters to measure 15N isotopic abundances in physiological samples:a pilot study on amino acid synthesis in the upper gastro-intestinal tract of minipigs[J].Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 1996, 31(4):367-376. doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-9888
[12] METGES C C, DAENZER M.13C gas chromatography-combustion isotope ratio mass spectrometry analysis of N-pivaloyl amino acid esters of tissue and plasma samples[J].Analytical Biochemistry, 2000, 278(2):156-164. doi: 10.1006/abio.1999.4426
[13] 王学敏.必需氨基酸和非必需氨基酸[J].国际检验医学杂志, 1984(6):30-31. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gwsq198406006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ [14] MCMAHON K W, FOGEL M L, ELSDON T S, et al.Carbon isotope fractionation of amino acids in fish muscle reflects biosynthesis and isotopic routing from dietary protein[J].Journal of Animal Ecology, 2010, 79(5):1132-1141. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2656.2010.01722.x
[15] CHOUDHARY N L, SAIRAM R K, TYAGI A.Expression of delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase gene during drought in rice (Oryza sativa L.)[J].Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics, 2005, 42(6):366-370. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=d7a084d8bcc04a53f6bcd0fee9fed479&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[16] YOSHIBA Y, KOYOSUE T, KATAGIRI T, et al.Correlation between the induction of a gene for delta 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase and the accumulation of proline in Arabidopsis thaliana under osmotic stress[J].The Plant Journal, 1995, 7(5):751-760. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1995.07050751.x
[17] SARADHI P P, ALIAARORA S, PRASAD K V S K.Proline accumulates in plants exposed to uv radiation and protects them against uv-induced peroxidation[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 1995, 209(1):1-5. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1461
[18] LARSEN T, TAYLOR D L, LEIGH M B, et al.Stable isotope fingerprinting:a novel method for identifying plant, fungal, or bacterial origins of amino acids[J].Ecology, 2009, 90(12):3526-3535. doi: 10.1890/08-1695.1
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 吴继法,赵艳芳. 基于铅稳定同位素比值和线性判别分析相结合的刺参产地溯源研究. 食品科技. 2023(12): 135-140 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 蒋冰雪,张晓梅,何晓霞,张九凯,张鸿伟,李兆杰,薛长湖,冯婷玉,姜晓明. 商品海参溯源分析技术研究进展. 食品科学. 2021(13): 309-318 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 唐华丽,高涛,王兆丹,罗振宇,罗黄洋. 稳定同位素比率质谱法在水产品溯源中的研究进展. 食品与发酵工业. 2020(10): 296-302 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 金俊,郑方媛,周秀雯,潘家荣. 稳定同位素指纹分析在车厘子产地溯源中的应用. 核农学报. 2020(08): 1722-1728 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 申兆栋,黄冬梅,蔡友琼,叶洪丽,田良良,习寅峰,张政权,伍姿,张俊. 氨基酸与脂肪酸指纹分析技术在农产品产地溯源中的应用研究. 农产品质量与安全. 2020(05): 80-85 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李政,赵姗姗,郄梦洁,王明林,陈爱亮,赵燕. 动物源性农产品产地溯源技术研究. 农产品质量与安全. 2019(03): 57-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张莹,王杰,杨娟,罗红玉,钟应富,袁林颖,徐泽,邬秀宏. 稳定同位素技术在农产品产地判别应用研究进展. 南方农业. 2019(34): 33-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载: